Traffic Management
Traffic Management Conceptual Overview
- Control Plane Policies: Control plane policy maps are applied to the control plane.
- QoS Policies: QoS policy maps are applied to Ethernet and port channel interfaces.
- Segment Routing Traffic Engineering Policy (SR-TE).
- PBR Policies: PBR policy maps are applied to Ethernet interfaces, port channel interfaces and switch virtual interfaces (SVIs).
- A class map is a data structure that defines a data stream by specifying characteristics of data packets that comprise that stream. Each class map is typed as either QoS, control plane, or PBR and is available only to identically typed policy maps.
- Traffic resolution commands specify data handling methods for traffic that matches a class map. Traffic resolution options vary by policy map type.
Data packets that enter an entity to which a policy map is assigned are managed with traffic resolution commands of the first class that matches the packets.
Control Plane Policies
The switch defines one control plane policy map named copp-system-policy. The copp-system-policy policy map always applies to the control plane and cannot be removed from the switch. Other control plane policy maps cannot be added. Copp-system-policy consists of preconfigured classes, each containing a static class map and traffic resolution commands. Preconfigured classes cannot be removed from copp-system-policy.
The switch provides static class maps and you cannot modify or delete them. The switch uses a naming convention of static class maps as copp-system- name, where name differentiates the class maps. Static class maps have pre-defined internal conditions, not based on ACLs, and only listed in running-config as components of copp-system-policy. The sequence of static class maps in the policy map is not significant. Traffic resolution commands define minimum (bandwidth) and maximum (shape) transmission rates for data streams matching the corresponding class map.
- Add classes consisting of an eponymous dynamic class map and traffic resolution
commands.
Create, edit, or delete dynamic class maps, and filter traffic with a single IPv4 ACL, and list in running-config.
- Change traffic resolution commands for a preconfigured class.
QoS Policies
QoS policy maps are user defined. The switch does not provide preconfigured QoS policy maps and in the default configuration, policy maps are not applied to any Ethernet or port channel interface. Policy maps and class maps are created and applied to interfaces through configuration commands.
A QoS policy map is composed of one or more classes. Each class contains an eponymous dynamic class map and traffic resolution commands. Dynamic class maps are user created, can be edited or deleted, filter traffic with a single IPv4 ACL, and are listed in running-config.
- Set the Layer 2 CoS field
- Set the DSCP value in the ToS byte
- Specify a traffic class queue
- The class-default class map matches all traffic except IPv4 or IPv6 traffic and is not editable.
- By default, class-default class contains no traffic resolution commands. Traffic resolution commands can be added through configuration commands.
Data packets that enter an interface to which a policy map is assigned are managed with traffic resolution commands that correspond to the first class that matches the packet.
Segment Routing Traffic Engineering Policy (SR-TE)
Segment Routing Traffic Engineering Policy (SR-TE) policy uses Segment Routing (SR) to enable a headend to steer traffic along any path without maintaining per flow state in every node based on the policy. Configuring SR policy for the MPLS dataplane (SR-MPLS) for Type-1 SR policy segments with BGP and locally configured policies as sources of SR policy is available on DCS-7500 and DCS-7280 family of switches.
SR Policy Overview
- Endpoint - An IPv4 or IPv6 address which refers to the destination of the policy. eos allows 0/0 and 0:: and calls these IP addresses null endpoints.
- Color - An unsigned 32-bit opaque numerical quantity. Define the semantic of a color as you prefer. It can refer to, for instance, an application or a type of traffic, such as low latency, or a geographical location.
- SID-lists (SLs) - An ordered list of Segment Identifiers. Each SID provides a MPLS label in the MPLS instantiation of SR). An SL encodes one path from the headend to the destination. Each SL has an optional weight attached to it for the purpose of Unequal Cost Multipath (UCMP) traffic distribution. The default value for SL weight is 1.
- Preference - An optional, unsigned 32-bit integer used in the candidate path selection algorithm to select the active candidate path. The default value for preference is 100.
- Binding SID (BSID) - an optional
SID.Note: In eos, a BSID is mandatory for each candidate path.
- BGP
- Single agent routing model (Ribd)
- Multi-agent routing model
- Local configuration using CLI
- Single agent routing model (Ribd)
- Multi-agent routing model
- Openconfig YANG models
- PCEPNote: eos does not support PCEP.
Identity of a Candidate Path
- The ASN in the Originator set to 0.
- The node address in the Originator set to 0.0.0.0.
- The discriminator set to the Preference
configured.Note: eos CLI allows configuring only one candidate path at a given preference and does not allow configuring the discriminator for a candidate path.
State of an SID List (SL)
- Valid - The top label of the SL resolves within the LFIB to the outgoing next hop(s), interface(s) and a label action.
- Invalid - The top label of the SL unresolvable to
the outgoing next hop(s), interface(s) and a label
action. An SL is also marked as invalid when the SL
is resolvable, but the resolved labeled stack
exceeds the platform’s maximum SID depth (SID), that
is, exceeds the maximum number of labels the
platform can push in to the outgoing
packet.Note: The state is either valid or invalid.
State of a Candidate Path
- Invalid - Not eligible to participate in the
best/active candidate path selection algorithm
because of one of the reasons below.
- Invalid constituent SLs in the candidate path.
- No Binding SID present in the candidate path.
- Binding SIDpresent but outside SRLB range for the candidate path.
- Valid - At least one valid SL has lost out to some other candidate path in the best / active candidate path selection algorithm.
- Active: - A valid candidate path exists and wins the best / active candidate path selection algorithm. The active candidate path installs in the switch hardware and forwards traffic.
State of an SR Policy
eos considers an SR policy as valid when at least one of its candidate paths is valid. Otherwise, the SR policy is invalid.
Resolution of an SL
An SL resolves if the top label (first SID) can be resolved in the system Labeled FIB (LFIB) to yield a nexthop and outgoing interface(s). The other labels in the SID-List do not play a part in resolution.
Best Candidate Path (Active Candidate Path) Selection Algorithm
- The candidate path with higher preference selected.
- Locally configured candidate path selected over a BGP learned path
- Lower originator selected in the following instances:
- Lower AS number of Originator field selected.
- Lower Node address of Originator field selected.
- Current active candidate path selected in the following instances:
The following displays the reason for not selecting a path as an active path for a specified policy.
switch#show traffic-engineering segment-routing policy endpoint <endpoint> color <color>Binding SID
- Stitch together multiple domains.
- Stitch together different traffic tunnels .
- Overcome label stack imposition limitation in hardware.
BSID Conflict Handling
Examples
- Between Policies - If the policy (E1, C1) becomes
eligible to be active first, then it installs in the LFIB
and the policy (E2,C2) whose best path(CP1) conflicts with
the Policy (E1, C1) and does not become active.
- Policy(E1, C1): CP1: Binding-SID 965536 (wins best path)
- Policy(E2, C2): CP1: Binding-SID 965536 (wins best path)
- CP2: Binding-SID 965537
- with another Application: The SR-TE policies have the lowest preference when a conflict exists with any other application in eos using the SRLB range. The candidate paths with the same binding-SID as that of an LFIB entry by another application, for example, static adjacency segment, remains invalid.
In both the cases, when the conflict no longer exists, the candidate paths re-evaluate and may become active.
SR Policies from a BGP peer (a controller, route reflector) received for installation at the headend by eos. It does not propagate the received policies to BGP peers nor does it originate SR Policies for transmission to BGP peers.
The following supports IPv4 or IPv6 peers which can be single hop or multi-hop iBGP or eBGP peers.
- SAFI 73 for AFI 1 and AFI 2: IPv4 and IPv6 policy
endpoints, with the encoding defined in section 2.1 of
Advertising Segment Routing Policies
in BGP.Note: The nexthop address-family must match the AFI of the NLRI.
- Sub-TLVs of Tunnel Encapsulation TLV of type 15 (SR-TE Policy
Type) of the Tunnel Encapsulation Path Attribute
- Preference (Sub-TLV Type 12)
- Binding SID (Sub-TLV Type 13) of length 2 or 6 bytes
- Segment List (Sub-TLV Type 128). The following
Segment List sub-TLVs are supported:
- Type 1 Segment (Sub-TLV type 1)
- Weight (Sub-TLV type 9)
- Explicit NULL Label Policy (Sub-TLV Type 14)
- SR Prefix SID (sub TLV 3 of TLV 149, TLV 150)
- SR Range - Contents of TLV 149, TLV 150 (multi-topology)
Route-Target and NO_ADVERTISE Community in SR-TE SAFI Updates
eos implements the Acceptance and Usability checks as defined in sections 4.2.1 and 4.2.2 of the IETF draft Advertising Segment Routing Policies in BGP. However eos skips matching the Route-Target with the router-ID of the headend if the SR-TE NLRI is tagged with NO_ADVERTISE community.
ECMP does not support SR-TE SAFI Paths
Path Selection within BGP
The IETF draft Advertising Segment Routing Policies in BGP supports passing multiple candidate paths from a single protocol source for an SR-TE policy path selection. Therefore, it includes a field distinguisher in the NLRI which can be unique for each controller to make BGP pass through the policies. However when multiple sources use the same distinguisher, BGP performs a path selection for the tuple: Endpoint, Color and Distinguisher. The best path for that tuple publishes to the SR-TE Policy Agent for selecting an Active path. The best bgp-best-path selection applies to SR-TE SAFI as well.
Error Handling / Edge Cases
- Weight 0: The IETF draft does not limit the range of SL weight to exclude weight 0. A SID-List with weight 0 is not used for forwarding so BGP module in eos does not pass on SID-Lists with weight 0 to the SR-TE policy agent. Such SID-Lists will be visible in show bgp sr-te commands but not in show traffic-engineering segment-routing policy commands.
- Empty SLs: Given the TLV encoding used to propagate SR Policies in BGP, it is possible to receive SID-Lists without SIDs. The BGP module in eos does not pass empty SID-Lists to SR-TE policy agent. Such SID-Lists are visible in show bgp sr-te commands but not in show traffic-engineering segment-routing policy commands.
- Non Type 1 segments: eos supports only Type-1
segments. When receiving a BGP update with a
SID-List that has non Type-1 segments, eos ignores
the entire SID-List and sends a
BGP-4-SRTE_IGNORED_SEGMENT_LIST_UNSUPPORTED_SEGMENTSsyslog. Such SID-Lists are not stored locally, and show bgp sr-te command does not display them.Note: The SID-Lists made up of all Type-1 segments pass to the SR-TE policy agent.
Steering Traffic into a Policy
Incoming label as BSID - Labelled Steering
At the headend when receiving a packet with a label stack with a BSID of an active CP of a valid SR Policy as the top label, the headend pops the label, and imposes the resolved label stack on the outgoing packet.
Example
For instance, an SR Policy with an active candidate path with BSID 965536 and SL with label stack [965540, 900001, 900002]. Assume that 965540 is an IS-IS SR Adjacency SID. An incoming packet has a label stack [965536, 100000] then the outgoing label stack consists of [900001, 900002, 100000].
Steering BGP learnt IP(v6) prefixes - IP Steering
Incoming label is BSID - Labelled Steering
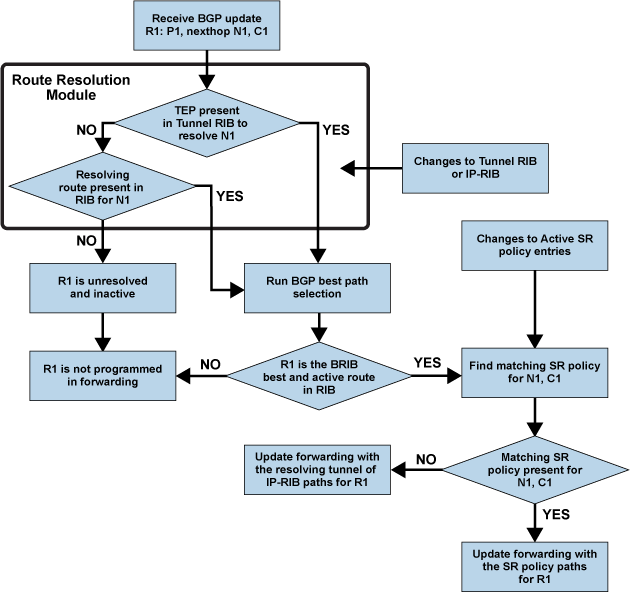
At the headend, BGP IPv4 and IPv6 routes receive one or more extended color communities and recursively resolves them through any active SR Policy that matches the BGP routes’ nexthop and color. When receiving an IPv4 or IPv6 packet forwarded using this policy, the SL’s resolved label stack imposes on the outgoing packet.
For BGP routes received with color community to be steered via an SR policy, the route’s nexthop must already be resolvable through IGP. If no resolving route exists in IGP, the route is considered unresolvable and does not program in hardware even if a matching SR policy existsfor the corresponding nexthop and color.
Color only IP steering using CO bits
It is possible to relax the requirement of an exact match of the BGP route’s nexthop with the endpoint of the SR Policy using the “CO” (Color Only) bits in the color extended community. The “CO” bits are 2 reserved bits repurposed for color only steering as defined in section 3 of Advertising Segment Routing Policies in BGP. The exact match of the nexthop is done with the CO bits set to 00 or 11.
- Active SR policy with endpoint N and color C
- Active SR policy with null endpoint (from the same AFI as the BGP route) and color C
- Active SR policy with null endpoint from any AFI and color C
- IGP route
CO = 10 Steering: in addition to the steps in CO = 01 steering, CO = 10 additionally relaxes the nexthop to match any endpoint. The following order is used for resolving a BGP route with nexthop N and color C. The behavior described is in accordance with section 8.8.1 of the IETF draft Segment Routing Policy for Traffic Engineering.
- Active SR policy with endpoint N and color C
- Active SR policy with null endpoint (from the same AFI as the BGP route) and color C
- Active SR policy with null endpoint from any AFI and color C
- Active SR policy for any endpoint from the same AFI as the BGP route and color C
- Active SR policy for any endpoint from any AFI and color C
- IGP route
ECMP of IPv4/IPv6 Prefixes that Resolve over SR-TE Policies
When multiple BGP paths of BGP unicast prefixes resolve through active SR policies form ECMP, the resulting FIB entry for the BGP route has an ECMP of segment list paths which is a union of all the segments-list entries present in each of the resolving SR policies for the BGP paths.
Example
The following table displays four paths for prefix 192.1.0.0/31, and each of the four paths resolves via SR-TE policies.
| Path | Nexthop | Color | Policy EP | Policy Color | Segment Lists | Per SL Traffic Distribution |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.0.0.2 | CO(00):1000 | 1.0.0.2 | 1000 | [2500 500], Weight: 1 [2501 500], Weight: 2 |
8.33% 16.66% |
| 2 | 1.0.2.2 | CO(00):2000 | 1.0.2.2 | 2000 | [2502 500], Weight: 1 [2503 500], Weight: 1 |
12.5% 12.5% |
| 3 | 1.0.4.2 | CO(00):3000 | 1.0.4.2 | 3000 | [2504 500], Weight: 1 [2505 500], Weight: 1 |
12.5% 12.5% |
| 4 | 1.0.6.2 | CO(00):4000 | 1.0.6.2 | 4000 | [2506 500], Weight: 1 [2507 500], Weight: 1 |
12.5% 12.5% |
B I 192.1.0.0/31 [200/0] via SR-TE Policy 1.0.4.2, color 3000
via SR-TE tunnel index 6, weight 1
via 1.0.4.2, Ethernet1, label 2505 500
via SR-TE tunnel index 5, weight 1
via 1.0.4.2, Ethernet1, label 2504 500
via SR-TE Policy 1.0.0.2, color 1000
via SR-TE tunnel index 2, weight 1
via 1.0.0.2, Ethernet2, label 2501 500
via SR-TE tunnel index 1, weight 1
via 1.0.0.2, Ethernet2, label 2500 500
via SR-TE Policy 1.0.2.2, color 2000
via SR-TE tunnel index 4, weight 1
via 1.0.2.2, Ethernet3, label 2503 500
via SR-TE tunnel index 3, weight 1
via 1.0.2.2, Ethernet3, label 2502 500
via SR-TE Policy 1.0.6.2, color 4000
via SR-TE tunnel index 8, weight 1
via 1.0.6.2, Ethernet6, label 2507 500
via SR-TE tunnel index 7, weight 1
via 1.0.6.2, Ethernet6, label 2506 500The traffic distribution honors the weights of the SID-Lists. In the example, each of the four SR Policies will get 25% of the total traffic meant for prefix 192.1.0.0/31. Within each policy, the distribution is based on the weights of the SID-Lists.
ECMP Group when some BGP unicast paths resolve over SR Policies and some via non SR Policy IGP paths
If some BGP paths resolve via SR Policy paths and some BGP paths resolve via non SR Policy IGP, then the ECMP group formed programmed as the active route in FIB, only considers the SR Policy paths. ECMP in the FIB is not formed between paths that resolve over SR Policy and paths that resolve via non SR Policy IGP routes. In the example above, if SR Policy with endpoint 1.0.6.2 and color 4000 becomes inactive or is removed, the FIB path for 192.1.0.0/31 resolves via 3 SR Policies as shown below.
B I 192.1.0.0/31 [200/0] via SR-TE Policy 1.0.4.2, color 3000
via SR-TE tunnel index 6, weight 1
via 1.0.4.2, Ethernet1, label 2505 500
via SR-TE tunnel index 5, weight 1
via 1.0.4.2, Ethernet1, label 2504 500
via SR-TE Policy 1.0.0.2, color 1000
via SR-TE tunnel index 2, weight 1
via 1.0.0.2, Ethernet2, label 2501 500
via SR-TE tunnel index 1, weight 1
via 1.0.0.2, Ethernet2, label 2500 500
via SR-TE Policy 1.0.2.2, color 2000
via SR-TE tunnel index 4, weight 1
via 1.0.2.2, Ethernet3, label 2503 500
via SR-TE tunnel index 3, weight 1
via 1.0.2.2, Ethernet3, label 2502 500UCMP of IPv4/IPv6 prefixes using LinkBandwidth (LBW) Extended Community that resolve over SR-TE policies not supported
When multiple BGP paths of BGP unicast prefixes resolve through active SR policies form ECMP, and the unicast paths also contain the LBW extended community, eos does not form UCMP amongst the unicast paths. Only ECMP is formed at the unicast prefix level. The LBW is ignored the behavior is identical to the behavior explained in the previous section.
Resolution of BGP unicast prefixes that resolve over other BGP unicast prefixes resolved via SR Policies
A BGP unicast prefix P1, that is recursively resolved via another BGP prefix P2, such that P2 resolves via an SR Policy, then in the FIB, P1 is programmed with the resolved nexthop pointing to the non SR Policy resolution of P2. P1 does not use P2s SR Policy for forwarding.
Explicit Null Label Imposition
When the address family of the BGP unicast prefix is not the same as the address family of the endpoint of the SR Policy that the unicast prefixes resolves via, an explicit null label is automatically imposed in the outgoing label stack.
Example
If an IPv4 unicast prefix P1 resolves over a policy whose endpoint EP1 is an IPv6 address (this can happen due to color only CO=01/10 steering with P1 having an IPv4 nexthop) and the SR Policy had a SID-List whose resolved label stack is [1001, 1002, 1003], the outgoing packet is imposed with [1001, 1002, 1003, 2] where 0 is the IPv4 explicit null label.
If an IPv6 prefix P2, resolves over a policy whose endpoint EP2 is an IPv4 address (this can happen with color only CO=01/10 steering with P2 having a IPv6 nexthop) and the SR Policy had a SID-List whose resolved label stack is [1001, 1002, 1003], the outgoing packet is imposed with [1001, 1002, 1003, 2] where 2 is the IPv6 explicit null label.
The following table lists the configurations which result in having explicit-null label in the resolved label stack.
| ENLP configuration for the resolving SR Policy | IPv4 Prefixes | IPv6 Prefixes |
|---|---|---|
| None | - | - |
| IPv4 | IPv4 explicit null appended to the end of label stack | - |
| IPv6 | - | IPv6 explicit null appended to the end of label stack |
| Both | IPv4 explicit null appended to the end of label stack | IPv6 explicit null appended to the end of label stack |
| No/Default config (incase of BGP learnt policies ENLP Sub-TLV is not received) | Resolving SR Policy has IPv4 Endpoint
address: No explicit-null |
Resolving SR Policy has IPv4 Endpoint
address: IPv6 explicit null appended to the end of label stack |
| Resolving SR Policy has IPv6 Endpoint
address: IPv4 explicit null appended to the end of label stack |
Resolving SR Policy has IPv6 Endpoint
address: No explicit-null |
Traffic Accounting
- 7280E/7500E systems: Up to 16k tunnels
- 7280R/7500R systems: Up to 8k tunnels
FEC Optimizations
- Programming of the active candidate path of an SR-TE policy in hardware is shared between the BSID route and IP steering route.
- If all of the following conditions are met, ISIS-SR MPLS
routes and tunnel entries directly point to the next
hop FEC generated by the routing agent (IGP FEC).
- All the next hops of the MPLS route either point to pop or forward (i.e. swapping to the same label) label action.
- The switch is either a 7280 or a 7500 platform.
- The corresponding SR-TE policy BSID routes (and corresponding Segment List tunnels) that resolve over ISIS-SR MPLS routes, will directly point to the IGP FEC.
Configuring SR-TE
switch(config)# router traffic-engineering
switch(config-te)# segment-routingswitch(config-te-sr)# policy endpoint v4Address|v6Address color color-value
switch(config-te-sr-policy)# binding-sid mpls-label
switch(config-te-sr-policy)# path-group preference valueswitch(config-te-sr-policy)# path-group preference value
switch(config-te-sr-policy-path)# segment-list label-stack label1 label2 … weight valueswitch(config-te-sr-policy-path)# explicit-null [none|ipv4|ipv6|both]BGP configuration for SR-TE SAFI
switch(config)# router bgp <as>
switch(config-router-bgp)# address-family ipv4|ipv6 sr-te
switch(config-router-bgp-af-srte)# neighbor neighbor activateswitch(config-router-bgp-af-srte)# neighbor neighbor route-map routeMapName inConfiguring Egress SR-TE Traffic Accounting
switch(config)# hardware counter feature mpls tunnelswitch# show hardware counter feature
Feature Direction Counter Resource (Engine)
------------------ ---------------- --------------------------
ACL-IPv4 out Jericho: 2, 3
ACL in Jericho: 4, 5, 6, 7
MPLS tunnel out Jericho: 8, 9switch(config)# no hardware counter feature mpls tunnelswitch# show bgp sr-te summary
BGP summary information for VRF default
Router identifier 100.1.1.2, local AS number 100
Neighbor Status Codes: m - Under maintenance
Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent InQ OutQ Up/Down State PfxRcd PfxAcc
100.1.1.1 4 100 407 413 0 0 00:18:57 Estab 1 1
1000::1 4 100 407 413 0 0 00:18:57 Estab 1 1switch# show bgp sr-te ipv4 summary
BGP summary information for VRF default
Router identifier 100.1.1.2, local AS number 100
Neighbor Status Codes: m - Under maintenance
Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent InQ OutQ Up/Down State PfxRcd PfxAcc
100.1.1.1 4 100 407 413 0 0 00:18:57 Estab 0 0switch# show bgp sr-te ipv6 summary
BGP summary information for VRF default
Router identifier 100.1.1.2, local AS number 100
Neighbor Status Codes: m - Under maintenance
Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent InQ OutQ Up/Down State PfxRcd PfxAcc
1000::1 4 100 407 413 0 0 00:18:57 Estab 0 0switch# show bgp sr-te
BGP routing table information for VRF default
Router identifier 100.1.1.1, local AS number 100
Policy status codes: * - valid, > - active, E - ECMP head, e - ECMP
c - Contributing to ECMP
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
AS Path Attributes: Or-ID - Originator ID, C-LST - Cluster List, LL Nexthop - Link Local Nexthop
Endpoint Color Distinguisher Next Hop Metric LocPref Weight Path
*> 133.1.1.1 0 1 130.1.1.3 0 100 0 ?
*> 133.1.1.1 0 2 130.1.1.3 0 100 0 ?
*> 1330::1 0 1 1300::3 0 100 0 ?
*> 1330::1 0 2 1300::3 0 100 0 ?switch# show bgp sr-te ipv4
BGP routing table information for VRF default
Router identifier 100.1.1.1, local AS number 100
Policy status codes: * - valid, > - active, E - ECMP head, e - ECMP
c - Contributing to ECMP
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
AS Path Attributes: Or-ID - Originator ID, C-LST - Cluster List, LL Nexthop - Link Local Nexthop
Endpoint Color Distinguisher Next Hop Metric LocPref Weight Path
*> 133.1.1.1 0 1 130.1.1.3 0 100 0 ?
*> 133.1.1.1 0 2 130.1.1.3 0 100 0 ?switch# show bgp sr-te ipv6
BGP routing table information for VRF default
Router identifier 100.1.1.1, local AS number 100
Policy status codes: * - valid, > - active, E - ECMP head, e - ECMP
c - Contributing to ECMP
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
AS Path Attributes: Or-ID - Originator ID, C-LST - Cluster List, LL Nexthop - Link Local Nexthop
Endpoint Color Distinguisher Next Hop Metric LocPref Weight Path
*> 1330::1 0 1 1300::3 0 100 0 ?
*> 1330::1 0 2 1300::3 0 100 0 ?switch# show bgp sr-te endpoint 133.1.1.1 color 0 distinguisher 1
BGP routing table information for VRF default
Router identifier 100.1.1.1, local AS number 100
BGP routing table entry for Endpoint: 133.1.1.1 Color: 0 Distinguisher: 1
Paths: 1 available
Local
130.1.1.3 from 100.1.1.2 (100.1.1.2)
Origin INCOMPLETE, metric 0, localpref 100, IGP metric 0, weight 0,
received 00:01:29 ago, valid, internal, best
Community: no-advertise
Rx SAFI: SR TE Policyswitch# show bgp sr-te endpoint 133.1.1.1 color 0 distinguisher 1 detail
BGP routing table information for VRF default
Router identifier 100.1.1.1, local AS number 100
BGP routing table entry for Endpoint: 133.1.1.1 Color: 0 Distinguisher: 1
Paths: 1 available
Local
130.1.1.3 from 100.1.1.2 (100.1.1.2)
Origin INCOMPLETE, metric 0, localpref 100, IGP metric 0, weight 0,
received 00:01:29 ago, valid, internal, best
Community: no-advertise
Rx SAFI: SR TE Policy
Tunnel encapsulation attribute: SR Policy
Preference: 200
Binding SID: 965536
Explicit null label policy: IPv4
Segment-List: Label Stack: [ 16004 16003 ], Weight: 10
Segment-List: Label Stack: [ 2000 3000 ]switch# show bgp neighbors 100.1.1.2 ipv4 sr-te policies
BGP routing table information for VRF default
Router identifier 100.1.1.1, local AS number 100
Policy status codes: * - valid, > - active
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
AS Path Attributes: Or-ID - Originator ID, C-LST - Cluster List, LL Nexthop - Link Local Nexthop
Endpoint Color Distinguisher Next Hop Metric LocPref Weight Path
*> 133.1.1.1 0 1 133.1.1.3 0 100 0 ?
*> 133.1.1.1 0 2 133.1.1.3 0 100 0 ?switch# show bgp neighbors 100.1.1.2 ipv4 sr-te policies detail
BGP routing table information for VRF default
Router identifier 100.1.1.1, local AS number 100
BGP routing table entry for Endpoint: 133.1.1.1 Color: 0 Distinguisher: 2
Paths: 1 available
Local
130.1.1.3 from 100.1.1.2 (100.1.1.2)
Origin INCOMPLETE, metric 0, localpref 100, IGP metric 0, weight 0,
received 00:01:29 ago, invalid, internal
Rx SAFI: SR TE Policy
Tunnel encapsulation attribute: SR Policy
Preference: 200
Binding SID: 965536
Explicit null label policy: IPv4
Segment-List: Label Stack: [ 16004 16003 ], Weight: 10
Segment-List: Label Stack: [ 2000 3000 ]PBR Policies
Policy-Based Routing (PBR) allows the operator to specify the next hop for selected incoming packets on an L3 interface, overriding the routing table. Incoming packets are filtered through a policy map referencing one or more ACLs, and matching packets are routed to the next hop specified.
A PBR policy map is composed of one or more classes and can include next-hop information for each class. It can also include single-line raw match statements, which have the appearance and function of a single line from an ACL. Each class contains an eponymous class map. Class maps are user-created, can be edited or deleted, filter traffic using IPv4 ACLs, and are listed in running-config.
Traffic Management Configuration Arad Platform Switches
Traffic policies are implemented by policy maps, which are applied to the control plane, or to L3 interfaces for Policy-Based Routing (PBR). Policy maps contain classes, which are composed of class maps and traffic resolution commands.
Traffic Management Conceptual Overview describes traffic policies.
Configuring Control Plane Traffic PoliciesArad Platform Switches
Default control plane traffic policies are implemented automatically without user intervention. These policies are modified by associating traffic resolution commands with static classes that comprise the control plane policy map.
Static Class Maps
Control plane traffic policies utilize static class maps, which are provided by the switch, are not editable, and cannot be deleted.
Editing the Policy Map
The only control plane policy map is copp-system-policy, which cannot be deleted. In its default form, copp-system-policy consists of the classes listed in class (policy-map (control-plane) Arad). Although the underlying class map of each class cannot be edited, the traffic resolution commands can be adjusted. The default classes cannot be removed from the policy map and their sequence within the policy map is not editable.
Policy maps are modified in policy-map configuration mode. The policy-map type copp command enters policy-map configuration mode.
Examples
switch(config)# policy-map type copp copp-system-policy
switch(config-pmap-copp-system-policy)#The class (policy-map (control-plane) Arad) command enters policy-map-class configuration mode, where traffic resolution commands are modified for the configuration mode class.
Example
switch(config-pmap-copp-system-policy)# class copp-system-lacp
switch(config-pmap-c-copp-system-policy-copp-system-lacp)#- bandwidth (policy-map-class (control-plane) Arad) specifies the minimum bandwidth.
- shape (policy-map-class (control-plane) Arad) specifies the maximum bandwidth.
Example
switch(config-pmap-c-copp-system-policy-copp-system-lacp)# bandwidth kbps 2000
switch(config-pmap-c-copp-system-policy-copp-system-lacp)# shape kbps 4000
switch(config-pmap-c-copp-system-policy-copp-system-lacp)#Policy-map and policy-map-class configuration modes are group-change modes. Changes are saved with the exit command or discarded with the abort command. The show active command displays the saved version of policy map. The show pending command displays the modified policy map.
Example
switch(config-pmap-c-copp-system-policy-copp-system-lacp)# exit
switch(config-pmap-copp-system-policy)# show pending
policy-map type copp copp-system-policy
class copp-system-bpdu
class copp-system-lldp
class copp-system-lacp
shape kbps 4000
bandwidth kbps 2000
class copp-system-l3ttl1
class copp-system-l3slowpath
switch(config-pmap-copp-system-policy)# exit
switch(config)#Applying Policy Maps to the Control Plane
The copp-system-policy policy map is always applied to the control plane. No commands are available to add or remove this assignment.
Displaying Policy Maps
The show policy-map interface type qos command displays the configured values of the policy maps classes and the number of packets filtered and dropped as a result of the class maps.
Example
switch(config)# show policy-map copp copp-system-policy
Service-policy input: copp-system-policy
Hardware programming status: InProgress
Class-map: copp-system-mlag (match-any)
shape : 10000001 kbps
bandwidth : 10000001 kbps
Out Packets : 0
Drop Packets : 0
Class-map: copp-system-bpdu (match-any)
shape : 2604 kbps
bandwidth : 1302 kbps
Out Packets : 0
Drop Packets : 0
Class-map: copp-system-lacp (match-any)
shape : 4230 kbps
bandwidth : 2115 kbps
Out Packets : 0
Drop Packets : 0
switch(config)#
switch(config-pmap-c-copp-system-policy-copp-system-lacp)# exitConfiguring QoS Traffic Policies Arad Platform Switches
QoS traffic policies are implemented by creating class maps and policy maps, then applying the policy maps to Ethernet and port channel interfaces.
Creating Class Maps
QoS traffic policies utilize dynamic class maps that are created and modified in class-map configuration mode. The class-map type qos command enters class-map configuration mode.
Example
switch(config)# class-map type qos match-any Q-CMap_1
switch(config-cmap-Q-CMap_1)#A class map contains one IPv4 access control list (ACL). The match ip access-group command assigns an ACL to the class map. Subsequent match commands replace the existing match command. Class maps filter traffic only on ACL permit rules. Deny ACL rules are disregarded.
Example
switch(config-cmap-Q-CMap_1)# match ip access-group ACL_1
switch(config-cmap-Q-CMap_1)#Class-map configuration mode is a group-change mode. Changes made in a group-change mode are saved by exiting the mode. The show active command displays the saved version of class map. The show pending command displays the unsaved class map.
Example
switch(config-cmap-Q-CMap_1)# show active
switch(config-cmap-Q-CMap_1)# show pending
class-map type qos match-any Q-CMap_1
match ip access-group ACL_1
switch(config-cmap-Q-CMap_1)#The exit command returns the switch to global configuration mode and saves pending class map changes. The abort command returns the switch to global configuration mode and discards pending changes.
Example
switch(config-cmap-CP-CMAP_1)# exit
switch(config)# show class-map type control-plane CP-CMAP_1
Class-map: CP-CMAP_1 (match-any)
Match: ip access-group name ACLv4_1
switch(config)#Creating Policy Maps
Policy maps are created and modified in policy-map configuration mode. The policy-map type quality-of-service command enters policy-map configuration mode.
Example
switch(config)# policy-map type quality-of-service Q-PMAP_1
switch(config-pmap-Q-PMAP_1)#Policy map are edited by adding or removing classes. A class automatically contains its eponymous class map; traffic resolution commands are added or edited in policy-map-class configuration mode. The below command adds a class to the configuration mode policy map and places the switch in policy-map-class configuration mode, where traffic resolution commands are added to the class.
Example
switch(config-pmap-Q-PMAP_1)# class Q-CMap_1
switch(config-pmap-c-Q-PMAP_1-Q-CMap_1)#- set cos sets the Layer 2 CoS field.
- set dscp sets the DSCP value in the ToS byte.
- set traffic class specifies a traffic class queue.
Example
switch(config-pmap-c-Q-PMAP_1-Q-CMap_1)# set cos 7
switch(config-pmap-c-Q-PMAP_1-Q-CMap_1)# set traffic-class 4
switch(config-pmap-c-Q-PMAP_1-Q-CMap_1)#Policy-map and policy-map-class configuration modes are group-change modes. Changes are saved with the exit command or discarded with the abort command. The show active and show pending commands display the saved and modified policy map versions, respectively.
Example
switch(config-pmap-c-Q-PMAP_1-Q-CMap_1)# exit
switch(config-pmap-Q-PMAP_1)# show pending
policy-map type quality-of-service Q-PMAP_1
class Q-CMap_1
set cos 7
set traffic-class 4
class class-default
switch(config-pmap-Q-PMAP_1)# exit
switch(config)#The last class in all QoS policy maps is class-default. The class-default class map matches all traffic except IPv4 or IPv6 traffic and provides no traffic resolution commands. The class-default class map is not editable; traffic resolution commands can be added to the class-default class.
To modify traffic resolution commands for the class-default class, enter policy-map-class configuration mode for the class, then enter the desired set commands.
Example
switch(config)# policy-map type quality-of-service Q-PMap_1
switch(config-pmap-Q-PMap_1)# class class-default
switch(config-pmap-c-Q-PMap_1-class-default)# set traffic-class 2
switch(config-pmap-c-Q-PMap_1-class-default)# exit
switch(config-pmap-Q-PMap_1)# exit
switch(config)# show policy-map type qos Q-PMap_1
Service-policy Q-PMap_1
Class-map: Q-CMap_1 (match-any)
Match: ipv6 access-group name ACLv6_1
set cos 7
set traffic-class 4
Class-map: class-default (match-any)
set traffic-class 2
switch(config)#Applying Policy Maps to an Interface
The service-policy type qos (Interface mode) command applies a specified policy map to the configuration mode interface.
switch(config)# interface ethernet 8
switch(config-if-Et8)# show active
switch(config-if-Et8)# service-policy input PMAP-1
switch(config-if-Et8)# show active
interface Ethernet8
service-policy type qos input PMAP-1
switch(config-if-Et8)#Configuring PBR Policies Arad Platform Switches
Policy-Based Routing (PBR) is implemented by creating class maps and policy maps, then applying the policy maps to Ethernet interfaces, port channel interfaces or switch virtual interfaces (SVIs).
Creating PBR Class Maps
PBR policies utilize class maps that are created and modified in the class-map configuration mode. The class-map type pbr command enters the class-map configuration mode.
Example
switch(config)# class-map type pbr match-any CMAP1
switch(config-cmap-PBR-CMAP1)#A class map contains one or more access control lists (ACLs). The match (policy-map (pbr)) command assigns an ACL to the class map. Subsequent match commands add additional ACLs to the class map. Class maps filter traffic only on ACL permit rules. Deny ACL rules are disregarded; if a class map includes ACLs with deny rules, the configuration reverts to its previous state.
Example
switch(config-cmap-PBR-CMAP1)# match ip access-group ACL1
switch(config-cmap-PBR-CMAP1)#The class-map configuration mode is a group-change mode. Changes made in a group-change mode are saved by exiting the mode. The show active command displays the saved version of class map.
switch(config-cmap-PBR-CMAP1)# show active
switch(config-cmap-PBR-CMAP1)#The exit command returns the switch to the global configuration mode and saves pending class map changes. The abort command returns the switch to the global configuration mode and discards pending changes.
Example
switch(config-cmap-PBR-CMAP1)# exit
switch(config)# show class-map type pbr CMAP1
class-map type pbr match-any CMAP1
10 match ip access-group ACL1
switch(config)#Creating PBR Policy Maps
Policy maps are created and modified in policy-map configuration mode. The policy-map type pbr command enters the policy-map configuration mode.
Example
switch(config)# policy-map type pbr PMAP1
switch(config-pmap-PMAP1)#Policy map are edited by adding or removing classes. A class automatically contains its eponymous class map; next-hop commands are added or edited in the policy-map-class configuration mode. The class (policy-map (pbr)) command adds a class to the configuration mode policy map and places the switch in the policy-map-class configuration mode, where next-hop commands are added to the class.
-
This command adds the CMAP1 class to the policy map and places the switch into the policy-map-class configuration mode.
switch(config-pmap-PMAP1)# class CMAP1 switch(config-pmap-c-PMAP1-CMAP1)#The set nexthop (policy-map-class pbr) command configures the next hop for data that passes the class map.
-
This command configures the policy map to set the next hop to 10.12.0.5 on packets filtered by the class map.
switch(config-pmap-c-PMAP1-CMAP1)# set nexthop 10.12.0.5 switch(config-pmap-c-PMAP1-CMAP1)#The set nexthop-group (policy-map-class(pbr) Arad) command configures a nexthop group as the next hop for data that passes the class map.
- These commands configure the policy map PMAP1 to set
the next hop to a nexthop group named GROUP1 for traffic
defined by class map CMAP1.
switch(config)# policy-map type pbr PMAP1 switch(config-pmap-PMAP1)# class CMAP1 switch(config-pmap-c-PMAP1-CMAP1)# set nexthop-group GROUP1 switch(config-pmap-c-PMAP1-CMAP1)#The policy-map and policy-map-class configuration modes are group-change modes. Changes are saved with the exit command or discarded with the abort command. The show active command displays the currently saved map version.
-
These commands exits the policy-map-class configuration mode, then exits the policy-map configuration mode to save the altered policy map to running-config.
switch(config-pmap-c-PMAP1-CMAP1)# exit switch(config-pmap-PMAP1)# exit switch(config)#
Applying a PBR Policy Map to an Interface
The service-policy type pbr (Interface mode) command applies the specified PBR policy map to the configuration mode interface. Only one PBR service policy is supported per interface.
switch(config)# interface ethernet 8
switch(config-if-Et8)# service-policy type pbr input PMAP1
switch(config-if-Et8)#Hardware Decapsulation
When hardware decapsulation takes place, PBR policy maps on Arad platform switches match on outer packet headers (i.e., they match based on the attributes of the packet before it is decapsulated).
Traffic Management Configuration FM6000 Platform Switches
Traffic policies are implemented by policy maps, which are applied to the control plane or an interface. Policy maps contain classes, which are composed of class maps and traffic resolution commands. Traffic Management Conceptual Overview describes traffic policies.
- Control plane policies manage control plane traffic.
- QoS traffic policies manage traffic on Ethernet and port channel interfaces.
Configuring Control Plane Traffic PoliciesFM6000 Platform Switches
Default control plane traffic policies are implemented automatically without user intervention. These policies are modified by associating traffic resolution commands with static classes that comprise the control plane policy map.
Static Class Maps
Control plane traffic policies utilize static class maps, which are provided by the switch, are not editable, and cannot be deleted.
Editing the Policy Map
The only control plane policy map is copp-system-policy, which cannot be deleted. In its default form, copp-system-policy consists of the classes listed in copp-system-policy default classes: FM6000 Platform Switches. Although the underlying class map of each class cannot be edited, the traffic resolution commands can be adjusted. The default classes cannot be removed from the policy map and their sequence within the policy map is not editable.
| Class Name | shape (pps) | bandwidth (pps) |
|---|---|---|
| copp-system-arp | 10000 | 1000 |
| copp-system-default | 8000 | 1000 |
| copp-system-ipmcrsvd | 10000 | 1000 |
| copp-system-ipmcmiss | 10000 | 1000 |
| copp-system-igmp | 10000 | 1000 |
| copp-system-l2rsvd | 10000 | 10000 |
| copp-system-l3slowpath | 10000 | 1000 |
| copp-system-pim-ptp | 10000 | 1000 |
| copp-system-ospf-isis | 10000 | 1000 |
| copp-system-selfip | 5000 | 5000 |
| copp-system-selfip-tc6to7 | 5000 | 5000 |
| copp-system-sflow | 25000 | 1000 |
Policy maps are modified in the policy-map configuration mode. The policy-map type copp command enters the policy-map configuration mode.
Example
switch(config)# policy-map type copp copp-system-policy
switch(config-pmap-copp-system-policy)#The class (policy-map (control-plane) FM6000) command enters the policy-map-class configuration mode, where traffic resolution commands are modified for the configuration mode class.
Example
switch(config-pmap-copp-system-policy)# class copp-system-arp
switch(config-pmap-c-copp-system-policy-copp-system-arp)#Example
switch(config-pmap-c-copp-system-policy-copp-system-arp)# bandwidth pps 2000
switch(config-pmap-c-copp-system-policy-copp-system-arp)# shape pps 4000
switch(config-pmap-c-copp-system-policy-copp-system-arp)#The policy-map and policy-map-class configuration modes are group-change modes. Changes are saved with the exit command or discarded with the abort command. The show active command displays the saved version of policy map. The show pending command displays the modified policy map.
Example
switch(config-pmap-c-copp-system-policy-CP-CMAP_1)# exit
switch(config-pmap-copp-system-policy)# show pending
policy-map type copp copp-system-policy
class CP-CMAP_1
shape pps 4000
bandwidth pps 2000
class copp-system-bpdu
class copp-system-lldp
class copp-system-lacp
class copp-system-arp
class copp-system-arpresolver
class copp-system-default
switch(config-pmap-copp-system-policy)#exit
switch(config)#Applying Policy Maps to the Control Plane
The copp-system-policy policy map is always applied to the control plane. No commands are available to add or remove this assignment.
Configuring QoS Traffic Policies FM6000 Platform Switches
QoS traffic policies are implemented by creating class maps and policy maps, then applying the policy maps to Ethernet and port channel interfaces.
Creating Class Maps
QoS traffic policies utilize dynamic class maps that are created and modified in the class-map configuration mode. The class-map type qos command enters the class-map configuration mode.
Example
switch(config)# class-map type qos match-any Q-CMap_1
switch(config-cmap-Q-CMap_1)#A class map contains one IPv4 access control list (ACL). The match (class-map (qos) FM6000) command assigns an ACL to the class map. Subsequent match commands replace the existing match command. Class maps filter traffic only on ACL permit rules. Deny ACL rules are disregarded.
Example
switch(config-cmap-Q-CMap_1)# match ip access-group ACL_1
switch(config-cmap-Q-CMap_1)#The class-map configuration mode is a group-change mode. Changes made in a group-change mode are saved by exiting the mode. The show active command displays the saved version of class map. The show pending command displays the unsaved class map.
Example
switch(config-cmap-Q-CMap_1)# show active
switch(config-cmap-Q-CMap_1)# show pending
class-map type qos match-any Q-CMap_1
match ip access-group ACL_1
switch(config-cmap-Q-CMap_1)#The exit command returns the switch to the global configuration mode and saves pending class map changes. The abort command returns the switch to the global configuration mode and discards pending changes.
Example
switch(config-cmap-CP-CMAP_1)# exit
switch(config)# show class-map type control-plane CP-CMAP_1
Class-map: CP-CMAP_1 (match-any)
Match: ip access-group name ACLv4_1
switch(config)#Creating Policy Maps
Policy maps are created and modified in the policy-map configuration mode. The policy-map type quality-of-service command enters the policy-map configuration mode.
Example
switch(config)# policy-map type quality-of-service Q-PMAP_1
switch(config-pmap-Q-PMAP_1)#Policy map are edited by adding or removing classes. A class automatically contains its eponymous class map; traffic resolution commands are added or edited in the policy-map-class configuration mode. The class (policy-map (qos) FM6000) command adds a class to the configuration mode policy map and places the switch in the policy-map-class configuration mode, where traffic resolution commands are added to the class.
Example
switch(config-pmap-Q-PMAP_1)# class Q-CMap_1
switch(config-pmap-c-Q-PMAP_1-Q-CMap_1)#- set cos sets the Layer 2 CoS field.
- set dscp sets the DSCP value in the ToS byte.
- set traffic class specifies a traffic class queue.
Example
switch(config-pmap-c-Q-PMAP_1-Q-CMap_1)# set cos 7
switch(config-pmap-c-Q-PMAP_1-Q-CMap_1)# set traffic-class 4
switch(config-pmap-c-Q-PMAP_1-Q-CMap_1)#The policy-map and policy-map-class configuration modes are group-change modes. Changes are saved with the exit command or discarded with the abort command. The show active and show pending commands display the saved and modified policy map versions, respectively.
Example
switch(config-pmap-c-Q-PMAP_1-Q-CMap_1)# exit
switch(config-pmap-Q-PMAP_1)# show pending
policy-map type quality-of-service Q-PMAP_1
class Q-CMap_1
set cos 7
set traffic-class 4
class class-default
switch(config-pmap-Q-PMAP_1)# exit
switch(config)#The last class in all QoS policy maps is class-default. The class-default class map matches all traffic except IPv4 or IPv6 traffic and provides no traffic resolution commands. The class-default class map is not editable; traffic resolution commands can be added to the class-default class.
To modify traffic resolution commands for the class-default class, enter the policy-map-class configuration mode for the class, then enter the desired set commands.
Example
switch(config)# policy-map type quality-of-service Q-PMap_1
switch(config-pmap-Q-PMap_1) #class class-default
switch(config-pmap-c-Q-PMap_1-class-default)# set traffic-class 2
switch(config-pmap-c-Q-PMap_1-class-default)# exit
switch(config-pmap-Q-PMap_1)# exit
switch(config)# show policy-map type qos Q-PMap_1
Service-policy Q-PMap_1
Class-map: Q-CMap_1 (match-any)
Match: ipv6 access-group name ACLv6_1
set cos 7
set traffic-class 4
Class-map: class-default (match-any)
set traffic-class 2
switch(config)#Applying Policy Maps to an Interface
The service-policy type qos (Interface mode) command applies a specified policy map to the configuration mode interface.
These commands apply PMAP-1 policy map to interface ethernet 8.switch(config)# interface ethernet 8
switch(config-if-Et8)# show active
switch(config-if-Et8)# service-policy input PMAP-1
switch(config-if-Et8)# show active
interface Ethernet8
service-policy type qos input PMAP-1
switch(config-if-Et8)#Configuring PBR Policies FM6000 Platform Switches
Policy-Based Routing (PBR) is implemented by creating class maps and policy maps, then applying the policy maps to Ethernet interfaces, port channel interfaces or Switch Virtual Interfaces (SVIs).
Creating PBR Class Maps
PBR policies utilize class maps that are created and modified in the class-map configuration mode. The class-map type pbr command enters the class-map configuration mode.
Example
switch(config)# class-map type pbr match-any CMAP1
switch(config-cmap-PBR-CMAP1)#A class map contains one or more IPv4 access control lists (ACLs). The match (policy-map (pbr)) command assigns an ACL to the class map. Subsequent match commands add additional ACLs to the class map. Class maps filter traffic only on ACL permit rules. Deny ACL rules are disregarded; if a class map includes ACLs with deny rules, the configuration reverts to its previous state.
On FM6000 platform switches, counters are not supported, so a counters per-entry (ACL configuration modes) command in an ACL is ignored.
Example
switch(config-cmap-PBR-CMAP1)# match ip access-group ACL1
switch(config-cmap-PBR-CMAP1)#The class-map configuration mode is a group-change mode. Changes made in a group-change mode are saved by exiting the mode. The show active command displays the saved version of class map.
switch(config-cmap-PBR-CMAP1)# show active
switch(config-cmap-PBR-CMAP1)#The exit command returns the switch to global configuration mode and saves pending class map changes. The abort command returns the switch to global configuration mode and discards pending changes.
Example
switch(config-cmap-PBR-CMAP1)# exit
switch(config)# show class-map type pbr CMAP1
class-map type pbr match-any CMAP1
10 match ip access-group ACL1
switch(config)#Creating PBR Policy Maps
Policy maps are created and modified in the policy-map configuration mode. The policy-map type pbr command enters the policy-map configuration mode.
Example
switch(config)# policy-map type pbr PMAP1
switch(config-pmap-PMAP1)#Policy map are edited by adding or removing classes. A class automatically contains its eponymous class map; next-hop commands are added or edited in the policy-map-class configuration mode. The class (policy-map (pbr)) command adds a class to the configuration mode policy map and places the switch in the policy-map-class configuration mode, where next-hop commands are added to the class.
- This command adds the CMAP1 class to the policy map and
places the switch in the policy-map-class configuration
mode.
switch(config-pmap-PMAP1)# class CMAP1 switch(config-pmap-c-PMAP1-CMAP1)#The set nexthop (policy-map-class pbr) command configures the next hop for data that passes the class map.
- This command configures the policy map to set the next hop to
10.12.0.5 on packets filtered by the class
map.
switch(config-pmap-c-PMAP1-CMAP1)# set nexthop 10.12.0.5 switch(config-pmap-c-PMAP1-CMAP1)#The policy-map and policy-map-class configuration modes are group-change modes. Changes are saved with the exit command or discarded with the abort command. The show active command displays the currently saved map version.
Example
switch(config-pmap-c-PMAP1-CMAP1)# exit
switch(config-pmap-PMAP1)# exit
switch(config)#Applying a PBR Policy Map to an Interface
The service-policy type pbr (Interface mode) command applies the specified PBR policy map to the configuration mode interface. Only one PBR service policy is supported per interface.
switch(config)# interface ethernet 8
switch(config-if-Et8)# service-policy type pbr input PMAP1
switch(config-if-Et8)#Hardware Decapsulation
When hardware decapsulation takes place, PBR policy maps on FM6000 platform switches match on outer packet headers (i.e., they match based on the attributes of the packet before it is decapsulated).
Traffic Management Configuration Petra Platform Switches
Traffic policies are implemented by policy maps, which are applied to the control plane. Policy maps contain classes, which are composed of class maps and traffic resolution commands. QoS traffic policies are not supported on 7500 Series switches.
Traffic Management Conceptual Overview describes traffic policies.
Configuring Control Plane Traffic PoliciesPetra Platform Switches
Default control plane traffic policies are implemented automatically without user intervention. These policies are modified by associating traffic resolution commands with static classes that comprise the control plane policy map.
Static Class Maps
Control plane traffic policies utilize static class maps, which are provided by the switch, are not editable, and cannot be deleted.
Editing the Policy Map
The only control plane policy map is copp-system-policy, which cannot be deleted. In its default form, copp-system-policy consists of the classes listed in copp-system-policy default classes: Petra Platform Switches. Although the underlying class map of each class cannot be edited, the traffic resolution commands can be adjusted. The default classes cannot be removed from the policy map and their sequence within the policy map is not editable.
| Class Name | shape (kbps) | bandwidth (kbps) |
|---|---|---|
| copp-system-bpdu | 2500 | 1250 |
| copp-system-default | 2500 | 250 |
| copp-system-igmp | 2500 | 250 |
| copp-system-ipbroadcast | 2500 | 250 |
| copp-system-ipmc | 2500 | 250 |
| copp-system-ipmcmiss | 2500 | 250 |
| copp-system-ipmcrsvd | 2500 | 250 |
| copp-system-ipunicast | NO LIMIT | 250 |
| copp-system-l3destmiss | 2500 | 250 |
| copp-system-l3slowpath | 2500 | 250 |
| copp-system-l3ttl0 | 2500 | 250 |
| copp-system-l3ttl1 | 2500 | 250 |
| copp-system-lacp | 2500 | 1250 |
| copp-system-lldp | 2500 | 250 |
| copp-system-unicast-arp | 2500 | 250 |
Policy maps are modified in the policy-map configuration mode. The policy-map type copp command enters the policy-map configuration mode.
Example
switch(config)# policy-map type copp copp-system-policy
switch(config-pmap-copp-system-policy)#The class (policy-map (control-plane) Petra) command enters the policy-map-class configuration mode, where traffic resolution commands are modified for the configuration mode class.
- This command enters the policy-map-class
configuration mode for the copp-system-lldp static
class.
switch(config-pmap-copp-system-policy)# class copp-system-lldp switch(config-pmap-c-copp-system-policy-copp-system-lldp)#
- bandwidth (policy-map-class (control-plane) Petra) specifies the minimum bandwidth.
- shape (policy-map-class (control-plane) Petra) specifies the maximum bandwidth.
Example
switch(config-pmap-c-copp-system-policy-copp-system-lldp)# bandwidth kbps 2000
switch(config-pmap-c-copp-system-policy-copp-system-lldp)# shape kbps 4000
switch(config-pmap-c-copp-system-policy-copp-system-lldp)#The policy-map and policy-map-class configuration modes are group-change modes. Changes are saved with the exit command or discarded with the abort command. The show active command displays the saved version of policy map. The show pending command displays the configured policy map.
Petra platform switches do not support all discrete rate values. When a bandwidth or shape command specifies a value that is not supported, the switch converts the rate to the next highest discrete value that it supports. The show policy-map interface type qos command displays the converted rate and not the user configured rate.
Example
switch(config-pmap-c-copp-system-policy-copp-system-lacp)# exit
switch(config-pmap-copp-system-policy)# show pending
policy-map type copp copp-system-policy
class copp-system-bpdu
class copp-system-lldp
shape kbps 4000
bandwidth kbps 2000
class copp-system-lacp
switch(config-pmap-copp-system-policy)# exit
switch(config)#Changes are saved with the exit command or discarded with the abort command. The show active command displays the saved version of policy map. The show pending command displays the modified policy map.
Displaying Policy Maps
The show policy-map interface type qos command displays the traffic resolution rates of the policy maps classes and the number of packets filtered and dropped as a result of the class maps. The shape and bandwidth rates may differ from configured values, because the switch does not support all discrete rate values.
Example
switch(config)# show policy-map copp copp-system-policy
Service-policy input: copp-system-policy
Hardware programming status: InProgress
Class-map: copp-system-mlag (match-any)
shape : 10000001 kbps
bandwidth : 10000001 kbps
Out Packets : 0
Drop Packets : 0
Class-map: copp-system-lacp (match-any)
shape : 2604 kbps
bandwidth : 1302 kbps
Out Packets : 0
Drop Packets : 0
switch(config)#Applying Policy Maps to the Control Plane
The copp-system-policy policy map is always applied to the control plane. No commands are available to add or remove this assignment.
Configuring QoS Traffic Policies Petra Platform Switches
QoS traffic policies are not supported on Petra platform switches.
Configuring PBR Policies Petra Platform Switches
PBR policies are not supported on Petra platform switches.
Traffic Management Configuration Trident Platform Switches
Traffic policies are implemented by policy maps, which are applied to the control plane or an interface. Policy maps contain classes, which are composed of class maps and traffic resolution commands. Traffic Management Conceptual Overview describes traffic policies.
- Control plane policies manage control plane traffic.
- QoS traffic policies manage traffic on Ethernet and port channel interfaces.
Configuring Control Plane Traffic PoliciesTrident Platform Switches
Default control plane traffic policies are implemented automatically without user intervention. These policies are modified by creating class maps and editing the policy map to include the new class maps.
Creating Class Maps
Control plane traffic policies utilize static and dynamic class maps. Static class maps are provided by the switch, are not editable, and cannot be deleted. Dynamic class maps are created and modified in the class-map configuration mode. The class-map type copp command enters the class-map configuration mode.
Example
switch(config)# class-map type copp match-any CP-CMAP_1
switch(config-cmap-CP-CMAP_1)#Class maps contain one IPv4 or IPv6 access control list (ACL). The match (class-map (control-plane) Trident) command assigns an ACL to the class map. Subsequent match commands replace the existing match command. Class maps filter traffic only on ACL permit rules. Deny ACL rules are disregarded.
Example
switch(config-cmap-CP-CMAP_1)# match ip access-group ACLv4_1
switch(config-cmap-CP-CMAP_1)#The class-map configuration mode is a group-change mode. Changes are saved by exiting the mode. The show active command displays the saved version of class map. The show pending command displays the unsaved class map.
Example
switch(config-cmap-CP-CMAP_1)# show active
switch(config-cmap-CP-CMAP_1)# show pending
class-map type copp match-any CP-CMAP_1
match ip access-group ACLv4_1
switch(config-cmap-CP-CMAP_1)#The exit command returns the switch to the global configuration mode and saves pending class map changes. The abort command returns the switch to the global configuration mode and discards pending class map changes.
Example
switch(config-cmap-CP-CMAP_1)# exit
switch(config)# show class-map type control-plane CP-CMAP_1
Class-map: CP-CMAP_1 (match-any)
Match: ip access-group name ACLv4_1
switch(config)#Editing the Policy Map
The only control plane policy map is copp-system-policy, which cannot be deleted. In its default form, copp-system-policy consists of the classes listed in copp-system-policy default classes: Trident Platform Switches. Although the underlying class map of each class cannot be edited, the traffic resolution commands can be adjusted. The default classes cannot be removed from the policy map and their sequence within the policy map is not editable.
| Class Name | shape (pps) | bandwidth (pps) |
|---|---|---|
| copp-system-bpdu | 5000 | 5000 |
| copp-system-lacp | 5000 | 5000 |
| copp-system-selfip-tc6to7 | 5000 | 5000 |
| copp-system-selfip | 5000 | 5000 |
| copp-system-tc6to7 | 10000 | 1000 |
| copp-system-lldp | 10000 | 1000 |
| copp-system-ipmcrsvd | 10000 | 1000 |
| copp-system-igmp | 10000 | 1000 |
| copp-system-ipmcmiss | 10000 | 1000 |
| copp-system-glean | 10000 | 1000 |
| copp-system-tc3to5 | 10000 | 1000 |
| copp-system-arp | 10000 | 1000 |
| copp-system-arpresolver | 10000 | 1000 |
| copp-system-l3destmiss | 10000 | 1000 |
| copp-system-l3slowpath | 10000 | 1000 |
| copp-system-l3ttl1 | 10000 | 1000 |
| copp-system-default | 8000 | 1000 |
| copp-system-acllog | 10000 | 1000 |
| copp-system-sflow | 25000 | 0 |
Policy maps are modified in the policy-map configuration mode. The policy-map type copp command enters the policy-map configuration mode.
Example
switch(config)#policy-map type copp copp-system-policy
switch(config-pmap-copp-system-policy)#Dynamic classes are inserted in front of the static classes. Classes automatically contain their eponymous class map; traffic resolution commands are created or edited in the policy-map-class configuration mode. The class (policy-map (control-plane) Trident) command adds a class to the policy map and places the switch in the policy-map-class configuration mode, where traffic resolution commands are added to the class.
Example
switch(config-pmap-copp-system-policy)# class CP-CMAP_1
switch(config-pmap-c-copp-system-policy-CP-CMAP_1)#- bandwidth (policy-map-class (control-plane) Trident) specifies the minimum bandwidth.
- shape (policy-map-class (control-plane) Trident) specifies the maximum bandwidth.
Example
switch(config-pmap-c-copp-system-policy-CP-CMAP_1)# bandwidth pps 2000
switch(config-pmap-c-copp-system-policy-CP-CMAP_1)# shape pps 4000
switch(config-pmap-c-copp-system-policy-CP-CMAP_1)#The policy-map and policy-map-class configuration modes are group-change modes. Changes are saved with the exit command or discarded with the abort command. The show active command displays the saved version of policy map. The show pending command displays the modified policy map.
Example
switch(config-pmap-c-copp-system-policy-CP-CMAP_1)# exit
switch(config-pmap-copp-system-policy)# show pending
policy-map type copp copp-system-policy
class CP-CMAP_1
shape pps 4000
bandwidth pps 2000
class copp-system-bpdu
class copp-system-lldp
class copp-system-lacp
class copp-system-arp
class copp-system-arpresolver
class copp-system-default
switch(config-pmap-copp-system-policy)# exit
switch(config)#To modify traffic resolution commands for a static class, enter the policy-map-class configuration mode for the class, then enter the desired bandwidth and shape commands.
Example
switch(config)# policy-map type copp copp-system-policy
switch(config-pmap-copp-system-policy)# class copp-system-bpdu
switch(config-pmap-c-copp-system-policy-copp-system-bpdu)# shape pps 200
switch(config-pmap-c-copp-system-policy-copp-system-bpdu)# bandwidth pps 100
switch(config-pmap-c-copp-system-policy-copp-system-bpdu)# exit
switch(config-pmap-copp-system-policy)# show pending
policy-map type copp copp-system-policy
class CP-CMAP_1
shape pps 4000
bandwidth pps 2000
class copp-system-bpdu
shape pps 200
bandwidth pps 100
class copp-system-lldp
switch(config-pmap-copp-system-policy)# exit
switch(config)#Applying Policy Maps to the Control Plane
The copp-system-policy policy map is always applied to the control plane. No commands are available to add or remove this assignment.
Configuring QoS Traffic Policies Trident Platform Switches
QoS traffic policies are implemented by creating class maps and policy maps, then applying the policy maps to Ethernet and port channel interfaces.
Creating Class Maps
QoS traffic policies utilize dynamic class maps that are created and modified in the class-map configuration mode. The class-map type qos command enters the class-map configuration mode.
Example
switch(config)# class-map type qos match-any Q-CMap_1
switch(config-cmap-Q-CMap_1)#A class map contains one IPv4 or IPv6 Access Control List (ACL). The match (class-map (qos) Trident) command assigns an ACL to the class map. Subsequent match commands replace the existing match command. Class maps filter traffic only on ACL permit rules. Deny ACL rules are disregarded.
Example
switch(config-cmap-Q-CMap_1)# match ipv6 access-group ACLv6_1
switch(config-cmap-Q-CMap_1)#The class-map configuration mode is a group-change mode. Changes made in a group-change mode are saved by exiting the mode. The show active command displays the saved version of class map. The show pending command displays the unsaved class map.
Example
switch(config-cmap-Q-CMap_1)# show active
switch(config-cmap-Q-CMap_1)# show pending
class-map type qos match-any Q-CMap_1
match ipv6 access-group ACLv6_1
switch(config-cmap-Q-CMap_1)#The exit command returns the switch to global configuration mode and saves pending class map changes. The abort command returns the switch to global configuration mode and discards pending class map changes.
Example
switch(config-cmap-CP-CMAP_1)# exit
switch(config)# show class-map type control-plane CP-CMAP_1
Class-map: CP-CMAP_1 (match-any)
Match: ip access-group name ACLv4_1
switch(config)#Creating Policy Maps
Policy maps are created and modified in the policy-map configuration mode. The policy-map type quality-of-service command enters the policy-map configuration mode.
Example
switch(config)# policy-map type quality-of-service Q-PMAP_1
switch(config-pmap-Q-PMAP_1)#Policy maps are edited by adding or removing classes. A class automatically contains its eponymous class map; traffic resolution commands are added or edited in the policy-map-class configuration mode. The class (policy-map (qos) Trident) command adds a class to the configuration mode policy map and places the switch in the policy-map-class configuration mode, where traffic resolution commands are added to the class.
Example
switch(config-pmap-Q-PMAP_1)# class Q-CMap_1
switch(config-pmap-c-Q-PMAP_1-Q-CMap_1)#- set cos sets the layer 2 CoS field.
- set dscp sets the DSCP value in the ToS byte.
- set traffic class specifies a traffic class queue.
Example
switch(config-pmap-c-Q-PMAP_1-Q-CMap_1)# set cos 7
switch(config-pmap-c-Q-PMAP_1-Q-CMap_1)# set traffic-class 4
switch(config-pmap-c-Q-PMAP_1-Q-CMap_1)#The policy-map and policy-map-class configuration modes are group-change modes. Changes are saved with the exit command or discarded with the abort command. The show active and show pending commands display the saved and modified policy map versions, respectively.
Example
switch(config-pmap-c-Q-PMAP_1-Q-CMap_1)# exit
switch(config-pmap-Q-PMAP_1)# show pending
policy-map type quality-of-service Q-PMAP_1
class Q-CMap_1
set cos 7
set traffic-class 4
class class-default
switch(config-pmap-Q-PMAP_1)# exit
switch(config)#The last class in all QoS policy maps is class-default. The class-default class map matches all traffic except IPv4 or IPv6 traffic and provides no traffic resolution commands. The class-default class map is not editable; traffic resolution commands can be added to the class-default class.
To modify traffic resolution commands for the class-default class, enter the policy-map-class configuration mode for the class, then enter the desired set commands.
Example
switch(config)# policy-map type quality-of-service Q-PMap_1
switch(config-pmap-Q-PMap_1)# class class-default
switch(config-pmap-c-Q-PMap_1-class-default)# set traffic-class 2
switch(config-pmap-c-Q-PMap_1-class-default)# exit
switch(config-pmap-Q-PMap_1)# exit
switch(config)# show policy-map type qos Q-PMap_1
Service-policy Q-PMap_1
Class-map: Q-CMap_1 (match-any)
Match: ipv6 access-group name ACLv6_1
set cos 7
set traffic-class 4
Class-map: class-default (match-any)
set traffic-class 2
switch(config)#Applying Policy Maps to an Interface
The service-policy type qos (Interface mode) command applies a specified policy map to the configuration mode interface.
Example
switch(config)# interface ethernet 8
switch(config-if-Et8)# show active
switch(config-if-Et8)# service-policy input PMAP-1
switch(config-if-Et8)# show active
interface Ethernet8
service-policy type qos input PMAP-1
switch(config-if-Et8)#Configuring PBR Policies Trident Platform Switches
Policy-Based Routing (PBR) is implemented by creating class maps and policy maps, then applying the policy maps to Ethernet interfaces, port channel interfaces or Switch Virtual Interfaces (SVIs).
Creating PBR Class Maps
PBR policies utilize class maps that are created and modified in the class-map configuration mode. The class-map type pbr command enters the class-map configuration mode.
Example
switch(config)# class-map type pbr match-any CMAP1
switch(config-cmap-PBR-CMAP1)#A class map contains one or more Access Control Lists (ACLs). The match (policy-map (pbr)) command assigns an ACL to the class map. Subsequent match commands add additional ACLs to the class map. Class maps filter traffic only on ACL permit rules. Deny ACL rules are disregarded; if a class map includes ACLs with deny rules, the configuration reverts to its previous state.
Examples
- This command adds the ACL named ACL1 to the
class
map.
switch(config-cmap-PBR-CMAP1)# match ip access-group ACL1 switch(config-cmap-PBR-CMAP1)#The class-map configuration mode is a group-change mode. Changes made in a group-change mode are saved by exiting the mode. The show active command displays the saved version of class map.
- The show active command indicates that the configuration
mode class map is not stored in running-config.
switch(config-cmap-PBR-CMAP1)# show active switch(config-cmap-PBR-CMAP1)# - The exit command returns the switch to global configuration mode and saves pending class map changes. The abort command returns the switch to global configuration mode and discards pending changes.
- This command exits the class-map configuration mode and stores pending
changes to
running-config.
switch(config-cmap-PBR-CMAP1)# exit switch(config)# show class-map type pbr CMAP1 class-map type pbr match-any CMAP1 10 match ip access-group ACL1 switch(config)#
Creating PBR Policy Maps
Policy maps are created and modified in the policy-map configuration mode. The policy-map type pbr command enters policy-map configuration mode.
Examples
-
This command enters the policy-map configuration mode for creating a PBR policy map named PMAP1.
switch(config)# policy-map type pbr PMAP1 switch(config-pmap-PMAP1)#Policy map are edited by adding or removing classes. A class automatically contains its eponymous class map; next-hop commands are added or edited in the policy-map-class configuration mode. The class (policy-map (pbr)) command adds a class to the configuration mode policy map and places the switch in the policy-map-class configuration mode, where next-hop commands are added to the class.
- This command adds the CMAP1 class to the policy map and
places the switch in the policy-map-class configuration
mode.
switch(config-pmap-PMAP1)# class CMAP1 switch(config-pmap-c-PMAP1-CMAP1)# - The set nexthop (policy-map-class pbr) command
configures the next hop for data that passes the class map.This command configures
the policy map to set the next hop to 10.12.0.5 on packets
filtered by the class
map.
switch(config-pmap-c-PMAP1-CMAP1)# set nexthop 10.12.0.5 switch(config-pmap-c-PMAP1-CMAP1)# - The policy-map and policy-map-class configuration modes
are group-change modes. Changes are saved with the exit
command or discarded with the abort command. The
show active command displays the currently saved map
version. These commands exits the policy-map-class configuration mode,
then exits the policy-map configuration mode to save the altered policy
map to
running-config.
switch(config-pmap-c-PMAP1-CMAP1)# exit switch(config-pmap-PMAP1)# exit switch(config)#
Applying a PBR Policy Map to an Interface
- These commands apply the PMAP1 PBR policy map to
interface ethernet
8.
switch(config)# interface ethernet 8 switch(config-if-Et8)# service-policy type pbr input PMAP1 switch(config-if-Et8)#
Hardware Decapsulation
When hardware decapsulation takes place, PBR policy maps on Trident platform switches match on inner packet headers (i.e., they match based on the attributes of the decapsulated packet).
Traffic Management Configuration Trident II Platform Switches
Traffic policies are implemented by policy maps, which are applied to the control plane or an interface. Policy maps contain classes, which are composed of class maps and traffic resolution commands. Traffic Management Conceptual Overview describes traffic policies.
- Control plane policies manage control plane traffic.
- QoS traffic policies manage traffic on Ethernet and port channel interfaces.
Configuring Control Plane Traffic PoliciesTrident II Platform Switches
Default control plane traffic policies are implemented automatically without user intervention. These policies are modified by associating traffic resolution commands with static classes that comprise the control plane policy map.
Static Class Maps
Control plane traffic policies utilize static class maps, which are provided by the switch, are not editable, and cannot be deleted.
Editing the Policy Map
The only control plane policy map is copp-system-policy, which cannot be deleted. In its default form, copp-system-policy consists of the classes listed in copp-system-policy default classes: Trident II Platform Switches. Although the underlying class map of each class cannot be edited, the traffic resolution commands can be adjusted. The default classes cannot be removed from the policy map and their sequence within the policy map is not editable.
| Class Name | shape (pps) | bandwidth (pps) |
|---|---|---|
| copp-system-acllog | 1000 | 10000 |
| copp-system-arp | 1000 | 10000 |
| copp-system-arpresolver | 1000 | 10000 |
| copp-system-bfd | 5000 | 10000 |
| copp-system-bgp | 5000 | 5000 |
| copp-system-bpdu | 5000 | 5000 |
| copp-system-default | 1000 | 8000 |
| copp-system-glean | 1000 | 10000 |
| copp-system-igmp | 1000 | 10000 |
| copp-system-ipmcmiss | 1000 | 10000 |
| copp-system-ipmcrsvd | 1000 | 10000 |
| copp-system-l3destmiss | 1000 | 10000 |
| copp-system-l3slowpath | 1000 | 10000 |
| copp-system-l3ttl1 | 1000 | 10000 |
| copp-system-lacp | 5000 | 5000 |
| copp-system-lldp | 1000 | 10000 |
| copp-system-mlag | 5000 | 5000 |
| copp-system-selfip | 5000 | 5000 |
| copp-system-selfip-tc6to7 | 5000 | 5000 |
| copp-system-sflow | 0 | 25024 |
| copp-system-tc3to5 | 1000 | 10000 |
| copp-system-tc6to7 | 1000 | 10000 |
| copp-system-urm | 1000 | 10000 |
Policy maps are modified in the policy-map configuration mode. The policy-map type copp command enters the policy-map configuration mode.
- This command enters the policy-map configuration mode for
editing
copp-system-policy.
switch(config)# policy-map type copp copp-system-policy switch(config-pmap-copp-system-policy)# - The class (policy-map (control-plane) Trident II) command enters the policy-map-class configuration mode, where traffic resolution commands are modified for the configuration mode class.
- This command enters the policy-map-class configuration mode
for the copp-system-lacp static
class.
switch(config-pmap-copp-system-policy)# class copp-system-lacp switch(config-pmap-c-copp-system-policy-copp-system-lacp)#
- bandwidth (policy-map-class (control-plane) Trident II) specifies the minimum bandwidth.
- shape (policy-map-class (control-plane) Trident II) specifies the maximum bandwidth.
- These commands configure a bandwidth range of 2000
to 4000 packets per seconds (pps) for traffic
filtered by the copp-system-lacp class
map:
switch(config-pmap-c-copp-system-policy-copp-system-lacp)# bandwidth pps 2000 switch(config-pmap-c-copp-system-policy-copp-system-lacp)# shape pps 4000 switch(config-pmap-c-copp-system-policy-copp-system-lacp)# - The policy-map and policy-map-class configuration modes are group-change modes. Changes are saved with the exit command or discarded with the abort command. The show active command displays the saved version of policy map. The show pending command displays the modified policy map.
- These commands exits the policy-map-class configuration mode,
display the pending policy-map, then exit
policy-map configuration mode, which saves the altered
policy map to
running-config.
switch(config-pmap-c-copp-system-policy-copp-system-lacp)# exit switch(config-pmap-copp-system-policy)# show pending policy-map type copp copp-system-policy class copp-system-bpdu class copp-system-lldp class copp-system-lacp shape pps 4000 bandwidth pps 2000 class copp-system-arp switch(config-pmap-copp-system-policy)# exit switch(config)#
Applying Policy Maps to the Control Plane
The copp-system-policy policy map is always applied to the control plane. No commands are available to add or remove this assignment.
Traffic Management Configuration Commands
Traffic Policy (Control Plane) Configuration Commands
- bandwidth (policy-map-class (control-plane) Arad)
- bandwidth (policy-map-class (control-plane) FM6000)
- bandwidth (policy-map-class (control-plane) Helix)
- bandwidth (policy-map-class (control-plane) Petra)
- bandwidth (policy-map-class (control-plane) Trident)
- bandwidth (policy-map-class (control-plane) Trident II)
- class-map type copp
- class (policy-map (control-plane) Arad)
- class (policy-map (control-plane) FM6000)
- class (policy-map (control-plane) Helix)
- class (policy-map (control-plane) Petra)
- class (policy-map (control-plane) Trident)
- class (policy-map (control-plane) Trident II)
- match (class-map (control-plane) Helix)
- match (class-map (control-plane) Trident)
- match (class-map (control-plane) Trident II)
- policy-map type copp
- shape (policy-map-class (control-plane) Arad)
- shape (policy-map-class (control-plane) FM6000)
- shape (policy-map-class (control-plane) Helix)
- shape (policy-map-class (control-plane) Petra)
- shape (policy-map-class (control-plane) Trident)
- shape (policy-map-class (control-plane) Trident II)
Traffic Policy (PBR) Configuration Commands
- action set-ttl
- class (policy-map (pbr))
- class-map type pbr
- feature pbr
- match (class-map (pbr))
- match (policy-map (pbr))
- platform arad tcam counters feature
- policy-map type pbr
- resequence (class-map (pbr))
- resequence (policy-map (pbr))
- service-policy type pbr (Interface mode)
- set nexthop (policy-map-class pbr)
- set nexthop-group (policy-map-class(pbr) Arad)
CPU Traffic Policy Command
Traffic Policy (QoS) Configuration Commands
- class-map type qos
- class (policy-map (qos) FM6000)
- class (policy-map (qos) Helix)
- class (policy-map (qos) Trident)
- class (policy-map (qos) Trident II)
- match (class-map (qos) FM6000)
- match (class-map (qos) Helix)
- match (class-map (qos) Trident)
- match (class-map (qos) Trident II)
- policy-map type quality-of-service
- policy-map type quality-of-service policer
- service-policy type qos (Interface mode)
- set (policy-map-class (qos) FM6000)
- set (policy-map-class (qos) Helix)
- set (policy-map-class (qos) Trident)
- set (policy-map-class (qos) Trident II)
Traffic Policy Display and Utility Commands
- clear policy-map counters
- show class-map type control-plane
- show class-map type pbr
- show class-map type qos
- show policy-map type copp
- show policy-map type pbr
- show policy-map type qos
- show policy-map type qos counters
- show policy-map copp
- show policy-map interface type qos
- show policy-map interface type qos counters
- show traffic-policy
action set-ttl
The TTL action is effective only when it is configured along with a set nexthop or nexthop-group action. The TCAM profile has the set-ttl-3b or set-ttl action in the pbr ip and pbr ipv6 features, such as in the tc-counters system profile.
Command Mode
For IP
TCAM feature PBR IP configuration mode.
For IPv6
TCAM feature PBR IPv6 configuration mode.
Command Syntax
action set-time [set-ttl | set-ttl-3b]
no action set-time [set-ttl | set-ttl-3b]
default action set-time [set-ttl | set-ttl-3b]
Parameters
- set-ttl Set time to live.
- set-ttl-3b Set 3-bit time to live.
Examples
-
In the following example, for IP, the action sets the time to live for the next hop.
(config)# hardware tcam (config-tcam)# profile pbr-set-ttl copy default (config-tcam-profile-pbr-set-ttl)# feature pbr ip (config-tcam-feature-pbr-ip)# action set-ttl -
In the following example, for IPv6, the action sets the time to live for the next hop group.
config)# hardware tcam (config-tcam)# profile pbr-set-ttl copy default (config-tcam-profile-pbr-set-ttl)# feature pbr ip (config-tcam-feature-pbr-ip)# feature pbr ipv6 (config-tcam-feature-pbr-ipv6)# action set-ttl
bandwidth (policy-map-class (control-plane)Arad)
The bandwidth command specifies the minimum bandwidth for traffic filtered by the configuration mode policy map class.
The no bandwidth and default bandwidth commands remove the minimum bandwidth guarantee for the configuration mode class by deleting the corresponding bandwidth command from running-config.
Command Mode
Policy-map-class (control plane) configuration
accessed through class (policy-map (control-plane) Arad)
Command Syntax
bandwidth kbps kilobits
no bandwidth
default bandwidth
Parameters
kilobits Minimum data rate in kilobits per second. Value ranges from 1 to 10000000.
- class (policy-map (control-plane) Arad) places the switch in the policy-map-class (control plane) configuration mode.
- shape (policy-map-class (control-plane) Arad) specifies the maximum bandwidth for traffic defined by the associated class map in its configuration mode policy map class.
Static Classes Default Bandwidth
- copp-system-bgp 250 copp-system-l3lpmoverflow 250
- copp-system-bpdu 1250 copp-system-l3slowpath 250
- copp-system-default 250 copp-system-l3ttl1 250
- copp-system-ipbroadcast 250 copp-system-lacp 1250
- copp-system-ipmc 250 copp-system-linklocal 250
- copp-system-ipmcmiss 250 copp-system-lldp 250
- copp-system-ipunicast 250 copp-system-mlag 250
- copp-system-l2broadcast 250 copp-system-multicastsnoop 250
- copp-system-l2unicast 250 copp-system-OspfIsis 250
- copp-system-l3destmiss 250 copp-system-sflow 250
Example
switch(config)# policy-map type copp copp-system-policy
switch(config-pmap-copp-system-policy)# class copp-system-lldp
switch(config-pmap-c-copp-system-policy-copp-system-lldp)# bandwidth kbps 500
switch(config-pmap-c-copp-system-policy-copp-system-lldp)# exit
switch(config-pmap-copp-system-policy)# exit
switch(config)# show policy-map copp copp-system-policy
Service-policy input: copp-system-policy
Hardware programming status: InProgress
Class-map: copp-system-lldp (match-any)
shape : 2500 kbps
bandwidth : 500 kbps
Out Packets : 0
Drop Packets : 0
switch(config)#bandwidth (policy-map-class (control-plane)FM6000)
The bandwidth command specifies the minimum bandwidth for traffic filtered by the configuration mode policy map class.
The no bandwidth and default bandwidth commands remove the minimum bandwidth guarantee for the configuration mode class by deleting the corresponding bandwidth command from running-config.
Command Mode
Policy-map-class (control plane) configuration
accessed through class (policy-map (control-plane) FM6000)
Command Syntax
bandwidth pps packets
no bandwidth
default bandwidth
Parameters
packets Minimum data rate in packets per second. Value ranges from 1 to 100000.
- class (policy-map (control-plane) FM6000) places the switch in policy-map-class (control plane) configuration mode.
- shape (policy-map-class (control-plane) FM6000) specifies the maximum bandwidth for traffic defined by the associated class map in its configuration mode policy map class.
Static Classes Default Bandwidth
- copp-system-arp 1000 copp-system-l3slowpath 1000
- copp-system-default 1000 copp-system-pim-ptp 1000
- copp-system-ipmcrsvd 1000 copp-system-ospf-isis 1000
- copp-system-ipmcmiss 1000 copp-system-selfip 5000
- copp-system-igmp 1000 copp-system-selfip-tc6to7 5000
- copp-system-l2rsvd 10000 copp-system-sflow 1000
Example
switch(config)# policy-map type copp copp-system-policy
switch(config-pmap-copp-system-policy)# class PMAP-1
switch(config-pmap-c-copp-system-policy-PMAP-1)# bandwidth pps 1000
switch(config-pmap-c-copp-system-policy-PMAP-1)#bandwidth (policy-map-class (control-plane)Helix)
The bandwidth command specifies the minimum bandwidth for traffic filtered by the configuration mode policy map class.
The no bandwidth and default bandwidth commands remove the minimum bandwidth guarantee for the configuration mode class by deleting the corresponding bandwidth command from running-config.
Command Mode
Policy-map-class (control plane) configuration
accessed through class (policy-map (control-plane) Helix)
Command Syntax
bandwidth pps packets
no bandwidth
default bandwidth
Parameter
packets Minimum data rate in packets per second. Value ranges from 1 to 100000.
- class (policy-map (control-plane) Helix) places the switch in policy-map-class (control plane) configuration mode.
- shape (policy-map-class (control-plane) Helix) specifies the maximum bandwidth for traffic defined by the associated class map in its configuration mode policy map class.
Static Classes Default Bandwidth
- copp-system-acllog 1000 copp-system-l3ttl1 1000
- copp-system-arp 1000 copp-system-lacp 5000
- copp-system-arpresolver 1000 copp-system-lldp 1000
- copp-system-bfd 5000 copp-system-mlag 5000
- copp-system-bgp 5000 copp-system-OspfIsis 5000
- copp-system-bpdu 5000 copp-system-selfip 5000
- copp-system-default 1000 copp-system-selfip-tc6to7 5000
- copp-system-glean 1000 copp-system-sflow 0
- copp-system-igmp 1000 copp-system-tc3to5 1000
- copp-system-ipmcmiss 1000 copp-system-tc6to7 1000
- copp-system-ipmcrsvd 1000 copp-system-urm 1000
- copp-system-l3destmiss 1000 copp-system-vrrp 1000
- copp-system-l3slowpath 1000
Example
switch(config)# policy-map type copp copp-system-policy
switch(config-pmap-copp-system-policy)# class copp-system-lldp
switch(config-pmap-c-copp-system-policy-copp-system-lldp)# bandwidth pps 500
switch(config-pmap-c-copp-system-policy-copp-system-lldp)# exit
switch(config-pmap-copp-system-policy)# exit
switch(config)# show policy-map interface control-plan copp-system-policy
Service-policy input: copp-system-policy
Number of units programmed: 4
Hardware programming status: Successful
Class-map: copp-system-lldp (match-any)
shape : 10000 pps
bandwidth : 500 pps
Out Packets : 304996
Drop Packets : 0
switch(config)#bandwidth (policy-map-class (control-plane)Petra)
The bandwidth command specifies the minimum bandwidth for traffic filtered by the configuration mode policy map class.
The no bandwidth and default bandwidth commands remove the minimum bandwidth guarantee for the configuration mode class by deleting the corresponding bandwidth command from running-config.
Command Mode
Policy-map-class (control plane) configuration
accessed through class (policy-map (control-plane) Petra)
Command Syntax
bandwidth kbps kilobits
no bandwidth
default bandwidth
Parameter
kbits Minimum data rate in kilobits per second. Value ranges from 1 to 10000000.
- class (policy-map (control-plane) Petra) places the switch in policy-map-class (control plane) configuration mode.
- shape (policy-map-class (control-plane) Petra) specifies the maximum bandwidth for traffic defined by the associated class map in its policy map class configuration mode .
Static Classes Default Bandwidth
- copp-system-bpdu 1250 copp-system-l3destmiss 250
- copp-system-default 250 copp-system-l3slowpath 250
- copp-system-igmp 250 copp-system-l3ttl0 250
- copp-system-ipbroadcast 250 copp-system-l3ttl1 250
- copp-system-ipmc 250 copp-system-lacp 1250
- copp-system-ipmcmiss 250 copp-system-lldp 250
- copp-system-ipmcrsvd 250 copp-system-unicast-arp 250
- copp-system-ipunicast 250
Guidelines
Petra does not support all discrete rate values. When a specified discrete value is not supported, the switch converts the rate to the next highest discrete value that it supports. The show command displays the converted rate and not the user-configured rate.
Example
switch(config)# policy-map type copp copp-system-policy
switch(config-pmap-copp-system-policy)# class copp-system-lldp
switch(config-pmap-c-copp-system-policy-copp-system-lldp)# bandwidth kbps 500
switch(config-pmap-c-copp-system-policy-copp-system-lldp)# exit
switch(config-pmap-copp-system-policy)# exit
switch(config)# show policy-map copp copp-system-policy
Service-policy input: copp-system-policy
Hardware programming status: InProgress
Class-map: copp-system-lldp (match-any)
shape : 2766 kbps
bandwidth : 651 kbps
Out Packets : 0
Drop Packets : 0
switch(config)#bandwidth (policy-map-class (control-plane)Trident II)
The bandwidth command specifies the minimum bandwidth for traffic filtered by the configuration mode policy map class.
The no bandwidth and default bandwidth commands remove the minimum bandwidth guarantee for the configuration mode class by deleting the corresponding bandwidth command from running-config.
Command Mode
Policy-map-class (control plane) configuration
accessed through class (policy-map (control-plane) Trident II).
Command Syntax
bandwidth pps packets
no bandwidth
default bandwidth
Parameter
packets Minimum data rate in packets per second. Value ranges from 1 to 100000.
- class (policy-map (control-plane) Trident II) places the switch in policy-map-class (control plane) configuration mode.
- shape (policy-map-class (control-plane) Trident II) specifies the maximum bandwidth for traffic defined by the associated class map in its configuration mode policy map class.
Static Classes Default Bandwidth
- copp-system-acllog 1000 copp-system-l3slowpath 1000
- copp-system-arp 1000 copp-system-l3ttl1 1000
- copp-system-arpresolver 1000 copp-system-lacp 5000
- copp-system-bfd 5000 copp-system-lldp 1000
- copp-system-bgp 5000 copp-system-mlag 5000
- copp-system-bpdu 5000 copp-system-selfip 5000
- copp-system-default 1000 copp-system-selfip-tc6to7 5000
- copp-system-glean 1000 copp-system-sflow 0
- copp-system-igmp 1000 copp-system-tc3to5 1000
- copp-system-ipmcmiss 1000 copp-system-tc6to7 1000
- copp-system-ipmcrsvd 1000 copp-system-urm 1000
- copp-system-l3destmiss 1000
Example
switch(config)# policy-map type copp copp-system-policy
switch(config-pmap-copp-system-policy)# class copp-system-lldp
switch(config-pmap-c-copp-system-policy-copp-system-lldp)# bandwidth pps 500
switch(config-pmap-c-copp-system-policy-copp-system-lldp)# exit
switch(config-pmap-copp-system-policy)# exit
switch(config)# show policy-map interface control-plan copp-system-policy
Service-policy input: copp-system-policy
Number of units programmed: 4
Hardware programming status: Successful
Class-map: copp-system-lldp (match-any)
shape : 10000 pps
bandwidth : 500 pps
Out Packets : 304996
Drop Packets : 0
switch(config)#bandwidth (policy-map-class (control-plane)Trident)
The bandwidth command specifies the minimum bandwidth for traffic filtered by the configuration mode policy map class.
The no bandwidth and default bandwidth commands remove the minimum bandwidth guarantee for the configuration mode class by deleting the corresponding bandwidth command from running-config.
Command Mode
Policy-map-class (control plane) configuration
accessed through class (policy-map (control-plane) Trident).
Command Syntax
bandwidth pps packets
no bandwidth
default bandwidth
Parameter
packets Minimum data rate in packets per second. Value ranges from 1 to 100000.
- class (policy-map (control-plane) Trident) places the switch in policy-map-class (control plane) configuration mode.
- shape (policy-map-class (control-plane) Trident) specifies the maximum bandwidth for traffic defined by the associated class map in its configuration mode policy map class.
Static Classes Default Bandwidth
- copp-system-arp 1000 copp-system-lldp 1000
- copp-system-arpresolver 1000 copp-system-l3destmiss 1000
- copp-system-bpdu 5000 copp-system-l3slowpath 1000
- copp-system-default 1000 copp-system-l3ttl1 1000
- copp-system-glean 1000 copp-system-selfip 5000
- copp-system-igmp 1000 copp-system-selfip-tc6to7 5000
- copp-system-ipmcmiss 1000 copp-system-sflow 0
- copp-system-ipmcrsvd 1000 copp-system-tc6to7 1000
- copp-system-lacp 5000 copp-system-tc3to5 1000
Example
switch(config)# policy-map type copp copp-system-policy
switch(config-pmap-copp-system-policy)# class PMAP-1
switch(config-pmap-c-copp-system-policy-PMAP-1)# bandwidth pps 1000
switch(config-pmap-c-copp-system-policy-PMAP-1)#class (policy-map (control-plane) Arad)
The class command places the switch in policy-map-class (control plane) configuration mode, which is a group change mode for changing bandwidth and shape parameters associated with a specified class. All changes in a group change mode edit session are pending until the end of the session.
- The class map identifies a data stream.
- bandwidth command defines the streams minimum transmission rate through the control plane.
- shape command defines the streams maximum transmission rate through the control plane.
Static class maps identify a data stream by definition. Each data packet is managed by commands of the first class whose map matches the packets content. Dynamic classes are not supported for control plane policing on Arad platform switches.
Each class corresponds to a transmission queue. Queue scheduling is round-robin until bandwidth rate for a queue is exceeded. Scheduling becomes strict-priority with CPU queue number determining priority until the shape rate is reached. Packets are dropped after the shape rate is exceeded.
The exit command returns the switch to policy-map configuration mode. Saving policy-map-class changes also require an exit from policy-map mode, which saves pending policy-map-class and policy-map changes to running-config and returns the switch to the global configuration mode. The abort command discards pending changes, returning the switch to the global configuration mode.
The no class and default class commands remove policy-map-class commands for the specified class assignment from the policy map.
Command Mode
Policy-Map (control plane) configuration accessed through policy-map type copp command.
Command Syntax
class class_name
no class class_name
default class class_name
Parameter
class_name name of the class.Static Classes
- copp-system-bgp copp-system-l2broadcast copp-system-linklocal
- copp-system-bpdu copp-system-l2unicast copp-system-lldp
- copp-system-default copp-system-l3destmiss copp-system-mlag
- copp-system-ipbroadcast copp-system-l3lpmoverflow copp-system-multicastsnoop
- copp-system-ipmc copp-system-l3slowpath copp-system-OspfIsis
- copp-system-ipmcmiss copp-system-l3ttl1 copp-system-sflow
- copp-system-ipunicast copp-system-lacp
- bandwidth (policy-map-class (control-plane) Arad)
- shape (policy-map-class (control-plane) Arad)
- exit saves pending class map changes, then returns the switch to global configuration mode.
- abort discards pending class map changes, then returns the switch to global configuration mode.
Related Commands
policy-map type copp places switch in policy-map (control plane) configuration mode.Example
These commands enters policy-map-class configuration mode to modify the shape, bandwidth parameters associated with the static class named copp-system-lldp.switch(config)# policy-map type copp copp-system-policy
switch(config-pmap-copp-system-policy)# class copp-system-lldp
switch(config-pmap-c-copp-system-policy-copp-system-lldp)#class (policy-map (control-plane) FM6000)
The class command places the switch in policy-map-class (control plane) configuration mode, which is a group change mode for changing bandwidth and shape parameters associated with a specified class. All changes in a group change mode edit session are pending until the end of the session.
- The class map identifies a data stream.
- bandwidth command defines the streams minimum transmission rate through the control plane.
- shape command defines the streams maximum transmission rate through the control plane.
Static class maps identify a data stream by definition. Each data packet is managed by commands of the first class whose map matches the packets content. Dynamic classes are not supported for control plane policing on FM6000 platform switches.
Each class corresponds to a transmission queue. Queue scheduling is round-robin until bandwidth rate for a queue is exceeded. Scheduling becomes strict-priority with CPU queue number determining priority until the shape rate is reached. Packets are dropped after the shape rate is exceeded.
The exit command returns the switch to policy-map configuration mode. Saving policy-map-class changes also require an exit from policy-map mode, which saves pending policy-map-class and policy-map changes to running-config and returns the switch to the global configuration mode. The abort command discards pending changes, returning the switch to the global configuration mode.
The no class and default class commands remove policy-map-class commands for the specified class assignment from the policy map. The class is removed from the policy map if it is a dynamic class.
Command Mode
Policy-Map (control plane) configuration accessed through policy-map type copp command.
Command Syntax
class class_name
no class class_name
default class class_name
Parameter
class_name name of the class.Static Classes
- copp-system-arp copp-system-igmp copp-system-PimPtp
- copp-system-default copp-system-l2rsvd copp-system-selfip
- copp-system-ipmcmiss copp-system-l3slowpath copp-system-selfip-tc6to7
- copp-system-ipmcrsvd copp-system-OspfIsis copp-system-sflow
- bandwidth (policy-map-class (control-plane) FM6000)
- shape (policy-map-class (control-plane) FM6000)
- exit saves pending class map changes, then returns the switch to the global configuration mode.
- abort discards pending class map changes, then returns the switch to the global configuration mode.
Related Commands
policy-map type copp places switch in policy-map (control plane) configuration mode.Example
switch(config)# policy-map type copp copp-system-policy
switch(config-pmap-copp-system-policy)# class copp-system-arp
switch(config-pmap-c-copp-system-policy-copp-system-arp)#class (policy-map (control-plane) Helix)
The class command places the switch in policy-map-class (control plane) configuration mode, which is a group change mode for changing bandwidth and shape parameters associated with a specified class. All changes in a group change mode edit session are pending until the end of the session.
- The class map identifies a data stream.
- bandwidth command defines the streams minimum transmission rate through the control plane.
- shape command defines the streams maximum transmission rate through the control plane.
Static class maps identify a data stream by definition. Each data packet is managed by commands of the first class whose map matches the packets content. Dynamic classes are not supported for control plane policing on Helix platform switches.
Each class corresponds to a transmission queue. Queue scheduling is strict-priority; CPU queue number determines priority until the shape rate is reached. Packets are dropped after the shape rate is exceeded.
The exit command returns the switch to policy-map configuration mode. Saving policy-map-class changes also require an exit from policy-map mode, which saves the pending policy-map-class and policy-map changes to running-config and returns the switch to global configuration mode. The abort command discards pending changes, returning the switch to the global configuration mode.
The no class and default class commands remove the policy-map-class commands for the specified class assignment from the policy map.
Command Mode
Policy-Map (control plane) configuration accessed through policy-map type copp command.
Command Syntax
class class_name
no class class_name
default class class_name
Parameter
class_name name of the class.Static Classes
- copp-system-acllog copp-system-ipmcmiss copp-system-OspfIsis
- copp-system-arp copp-system-ipmcrsvd copp-system-selfip
- copp-system-arpresolver copp-system-l3destmiss copp-system-selfip-tc6to7
- copp-system-bfd copp-system-l3slowpath copp-system-sflow
- copp-system-bgp copp-system-l3ttl1 copp-system-tc3to5
- copp-system-bpdu copp-system-lacp copp-system-tc6to7
- copp-system-default copp-system-lldp copp-system-urm
- copp-system-glean copp-system-lldp copp-system-vrrp
- copp-system-igmp copp-system-lldp
- bandwidth (policy-map-class (control-plane) Helix)
- shape (policy-map-class (control-plane) Helix)
- exit saves pending class map changes, then returns the switch to the global configuration mode.
- abort discards pending class map changes, then returns the switch to the global configuration mode.
Related Commands
policy-map type copp places switch in policy-map (control plane) configuration mode.Example
switch(config)# policy-map
switch(config)# policy-map type copp copp-system-policy
switch(config-pmap-copp-system-policy)# class copp-system-lldp
switch(config-pmap-c-copp-system-policy-copp-system-lldp)#class (policy-map (control-plane) Petra)
The class command places the switch in policy-map-class (control plane) configuration mode, which is a group change mode for changing bandwidth and shape parameters associated with a specified class. All changes in a group change mode edit session are pending until the end of the session.
- The class map identifies a data stream.
- bandwidth command defines the streams minimum transmission rate through the control plane.
- shape command defines the streams maximum transmission rate through the control plane.
Static class maps identify a data stream by definition. Each data packet is managed by commands of the first class whose map matches the packets content. Dynamic classes are not supported for control plane policing on Petra platform switches.
Each class corresponds to a transmission queue. Queue scheduling is round-robin until bandwidth rate for a queue is exceeded. Scheduling becomes strict-priority with CPU queue number determining priority until the shape rate is reached. Packets are dropped after the shape rate is exceeded.
The exit command returns the switch to policy-map configuration mode. Saving the policy-map-class changes also require an exit from policy-map mode, which saves the pending policy-map-class and policy-map changes to running-config and returns the switch to the global configuration mode. The abort command discards pending changes, returning the switch to the global configuration mode.
The no class and default class commands remove the policy-map-class commands for the specified class assignment from the policy map.
Command Mode
Policy-Map (control plane) configuration accessed through policy-map type copp command.
Command Syntax
class class_name
no class class_name
default class class_name
Parameter
class_name name of the class.
Static Classes
- copp-system-bpdu copp-system-ipmcmiss copp-system-l3ttl0
- copp-system-default copp-system-ipmcrsvd copp-system-l3ttl1
- copp-system-igmp copp-system-ipunicast copp-system-lacp
- copp-system-ipbroadcast copp-system-l3destmiss copp-system-lldp
- copp-system-ipmc copp-system-l3slowpath copp-system-unicast-arp
- bandwidth (policy-map-class (control-plane) Petra)
- shape (policy-map-class (control-plane) Petra)
- exit saves pending class map changes, then returns the switch to the global configuration mode.
- abort discards pending class map changes, then returns the switch to the global configuration mode.
Related Commands
policy-map type copp places switch in policy-map (control plane) configuration mode.
Example
switch(config)# policy-map
switch(config)# policy-map type copp copp-system-policy
switch(config-pmap-copp-system-policy)# class copp-system-lldp
switch(config-pmap-c-copp-system-policy-copp-system-lldp)#class (policy-map (control-plane) Trident II)
The class command places the switch in policy-map-class (control plane) configuration mode, which is a group change mode for changing bandwidth and shape parameters associated with a specified class. All changes in a group change mode edit session are pending until the end of the session.
A policy map is an ordered list of classes. The control plane policy map contains 23 static classes. Each class contains an eponymous class map and may contain bandwidth and shape commands.
- The class map identifies a data stream.
- bandwidth command defines the streams minimum transmission rate through the control plane.
- shape command defines the streams maximum transmission rate through the control plane.
Static class maps identify a data stream by definition. Each data packet is managed by commands of the first class whose map matches the packets content. Dynamic classes are not supported for control plane policing on Trident II platform switches.
Each class corresponds to a transmission queue. Queue scheduling is strict-priority; CPU queue number determines priority until the shape rate is reached. Packets are dropped after the shape rate is exceeded.
The exit command returns the switch to the policy-map configuration mode. Saving the policy-map-class changes also require an exit from the policy-map mode, which saves the pending policy-map-class and policy-map changes to running-config and returns the switch to the global configuration mode. The abort command discards pending changes, returning the switch to the global configuration mode.
The no class and default class commands remove the policy-map-class commands for the specified class assignment from the policy map.
Command Mode
Policy-Map (control plane) configuration accessed through policy-map type copp command.
Command Syntax
class class_name
no class class_name
default class class_name
Parameter
class_name name of the class.Static Classes
- copp-system-acllog copp-system-igmp copp-system-mlag
- copp-system-arp copp-system-ipmcmiss copp-system-selfip
- copp-system-arpresolver copp-system-ipmcrsvd copp-system-selfip-tc6to7
- copp-system-bfd copp-system-l3destmiss copp-system-sflow
- copp-system-bgp copp-system-l3slowpath copp-system-tc3to5
- copp-system-bpdu copp-system-l3ttl1 copp-system-tc6to7
- copp-system-default copp-system-lacp copp-system-urm
- copp-system-glean copp-system-lldp
- bandwidth (policy-map-class (control-plane) Trident II)
- shape (policy-map-class (control-plane) Trident II)
- exit saves pending class map changes, then returns the switch to the global configuration mode.
- abort discards pending class map changes, then returns the switch to the global configuration mode.
Related Commands
policy-map type copp places switch in policy-map (control plane) configuration mode.Example
switch(config)# policy-map
switch(config)# policy-map type copp copp-system-policy
switch(config-pmap-copp-system-policy)# class copp-system-lldp
switch(config-pmap-c-copp-system-policy-copp-system-lldp)#class (policy-map (control-plane) Trident)
The class command places the switch in policy-map-class (control plane) configuration mode, which is a group change mode for changing bandwidth and shape parameters associated with a specified class. The command adds the specified class to the policy map if it was not previously included. All changes in a group change mode edit session are pending until the end of the session.
- The class map identifies a data stream.
- bandwidth command defines the streams minimum transmission rate through the control plane.
- shape command defines the streams maximum transmission rate through the control plane.
Dynamic class maps identify a data stream with an ACL assigned by match (class-map (control-plane) Trident). Static class maps identify a data stream by definition. Each data packet is managed by commands of the first class whose map matches the packets content.
Static classes are provided with the switch and cannot be removed from the policy map or modified by the class command. Dynamic classes are user defined and added to the policy map by this command. Dynamic classes are always placed in front of the static classes. Bandwidth and shape parameters are editable for all classes.
Each class corresponds to a transmission queue. Queue scheduling is round-robin until bandwidth rate for a queue is exceeded. Scheduling becomes strict-priority with CPU queue number determining priority until the shape rate is reached. Packets are dropped after the shape rate is exceeded.
The exit command returns the switch to policy-map configuration mode. Saving the policy-map-class changes also require an exit from policy-map mode, which saves the pending policy-map-class and policy-map changes to running-config and returns the switch to the global configuration mode. The abort command discards pending changes, returning the switch to the global configuration mode.
The no class and default class commands remove the policy-map-class commands for the specified class assignment from the policy map. The class is removed from the policy map if it is a dynamic class.
Command Mode
Policy-Map (control plane) configuration accessed through policy-map type copp command.
Command Syntax
class class_name [PLACEMENT]
no class class_name [PLACEMENT]
default class class_name [PLACEMENT]
- class_name name of the class.
- PLACEMENT Specifies the classs map placement.
Configurable only for dynamic classes.
- no parameter New classes are placed between the dynamic and static classes. Previously defined classes retain their current policy map placement.
- insert-before dynamic_class Class is inserted in front of the specified dynamic class.
Static Classes
- copp-system-acllog copp-system-ipmcmiss copp-system-lldp
- copp-system-arp copp-system-ipmcrsvd copp-system-selfip
- copp-system-arpresolver copp-system-l3destmiss copp-system-selfip-tc6to7
- copp-system-bpdu copp-system-l3slowpath copp-system-sflow
- copp-system-glean copp-system-l3ttl1 copp-system-tc3to5
- copp-system-igmp copp-system-lacp copp-system-tc6to7
- bandwidth (policy-map-class (control-plane) Trident)
- shape (policy-map-class (control-plane) Trident)
- exit saves pending class map changes, then returns the switch to the global configuration mode.
- abort discards pending class map changes, then returns the switch to the global configuration mode.
- class-map type copp places switch in the class-map (control-plane) configuration mode.
- policy-map type copp places switch in the policy-map (control plane) configuration mode.
Example
switch(config)# policy-map type copp copp-system-policy
switch(config-pmap-copp-system-policy)# class CM-1
switch(config-pmap-c-copp-system-policy-CM-1)#class (policy-map (pbr)
The class (policy-map (pbr) command places the switch in policy-map-class (pbr) configuration mode, which is a group change mode that modifies the specified class of the configuration mode Policy-Based Routing (PBR) policy map. The command adds the class to the policy map if it was not previously included in the policy map. All changes in a group change mode edit session are pending until the mode is exited, and can be canceled by using the abort command.
- The class map identifies a data stream through ACLs. Class maps are configured in the class-map (pbr) configuration mode.
- Set commands can be used to specify the next hop for a given class. Set commands are configured in policy-map-class (pbr) configuration mode.
PBR policy maps can also contain one or more raw match statements which filter incoming traffic without using ACLs. Data packets are managed by commands of the first class or raw match statement matching the packets contents.
The exit command returns the switch to the policy-map (pbr) configuration mode. However, saving the policy-map-class changes also requires an exit from policy-map (pbr) configuration mode. This saves all the pending policy map and policy-map-class changes to running-config and returns the switch to the global configuration mode. The abort command discards pending changes, returning the switch to the global configuration mode.
The no class and default class commands remove the class assignment from the configuration mode policy map by deleting the corresponding class configuration from running-config.
Command Mode
Policy-Map (pbr) Configuration accessed through policy-map type pbr.
Command Syntax
[sequence_number] class class_name
no [sequence_number] class class_name
default [sequence_number] class class_name
no [sequence_number]
default [sequence_number]
- sequence_number Sequence number (1 to 4294967295) assigned to the rule. If no number is entered, the number is derived by adding 10 to the number of the policy maps last numbered line. To increase the distance between existing entries, use the resequence command.
- class_name name of the class.
- set nexthop (policy-map-class pbr) sets next hop for the class.
- exit saves pending class changes and returns switch to policy-map (pbr) configuration mode.
- abort discards pending class changes and returns switch to policy-map (pbr) configuration mode.
- class-map type pbr places switch in the class-map (pbr) configuration mode.
- policy-map type pbr places switch in the policy-map (pbr) configuration mode.
Example
switch(config)# policy-map type pbr PMAP1
switch(config-pmap-PMAP1)# class CMAP1
switch(config-pmap-c-PMAP1-CMAP1)#class (policy-map (qos) FM6000)
The class command places the switch in policy-map-class (qos) configuration mode, which is a group change mode that modifies the specified class of the configuration mode policy map. The command adds the class to the policy map if it was not previously included in the policy map. All changes in a group change mode edit session are pending until the end of the session.
- The class map identifies a data stream through an ACL. Class maps are configured in the class-map (qos) configuration mode.
- Set commands either modify a packets content (CoS
or DSCP fields) or assigns it to a traffic class queue.
Set commands are configured in the
policy-map-class (qos) configuration mode.
Data packets are managed by commands of the first class whose map matches the packets content.
The exit command returns the switch to the policy-map configuration mode. However, saving policy-map-class changes also require an exit from the policy-map mode. This saves all pending policy map and policy-map-class changes to running-config and returns the switch to the global configuration mode. The abort command discards pending changes, returning the switch to the global configuration mode.
The no class and default class commands remove the class assignment from the configuration mode policy map by deleting the corresponding class configuration from running-config.
Command Mode
Policy-Map (qos) Configuration accessed through policy-map type quality-of-service.
Command Syntax
class class_name [PLACEMENT]
no class class_name [PLACEMENT]
default class class_name [PLACEMENT]
- class_name name of the class.
- PLACEMENT Specifies the map placement within the
list of class maps.
- no parameter Class is placed at the top of the list.
- insert-before existing_class Class is inserted in front of the specified class.
- set (policy-map-class (qos) FM6000)
- exit saves pending class changes and returns switch to policy-map (qos) configuration mode.
- abort discards pending class changes and returns switch to policy-map (qos) configuration mode.
Related Commands
- class-map type qos places switch in the class-map (QoS) configuration mode.
- policy-map type quality-of-service places switch in the policy-map (QoS) configuration mode
Example
switch(config)# policy-map type quality-of-service PMAP-1
switch(config-pmap-PMAP-1)# class CMAP-1
switch(config-pmap-c-PMAP-1-CMAP-1)#class (policy-map (qos) Helix)
The class command places the switch in the policy-map-class (QoS) configuration mode, which is a group change mode that modifies the specified class of the configuration mode policy map. The command adds the class to the policy map if it was not previously included in the policy map. All changes in a group change mode edit session are pending until the end of the session.
- The class map identifies a data stream through an ACL. Class maps are configured in the class-map (qos) configuration mode.
- Set commands either modify a packets content (CoS
or DSCP fields) or assigns it to a traffic class queue.
Set commands are configured in the
policy-map-class (qos) configuration mode.
Data packets are managed by commands of the first class whose map matches the packets content.
The exit command returns the switch to the policy-map configuration mode. However, saving policy-map-class changes also require an exit from the policy-map mode. This saves all the pending policy map and policy-map-class changes to running-config and returns the switch to the global configuration mode. The abort command discards pending changes, returning the switch to the global configuration mode.
The no class and default class commands remove the class assignment from the configuration mode policy map by deleting the corresponding class configuration from running-config.
Command Mode
Policy-Map (qos) Configuration accessed through policy-map type quality-of-service command.
Command Syntax
class class_name [PLACEMENT]
no class class_name [PLACEMENT]
default class class_name [PLACEMENT]
- class_name name of the class.
- PLACEMENT Specifies the map placement within the
list of class maps.
- no parameter Class is placed at the top of the list.
- insert-before existing_class Class is inserted in front of the specified class.
- set (policy-map-class (qos) Helix)
- exit saves pending class changes and returns switch to policy-map (qos) configuration mode.
- abort discards pending class changes and returns switch to policy-map (qos) configuration mode.
- class-map type qos places switch in the class-map (qos) configuration mode.
- policy-map type quality-of-service places switch in the policy-map (QoS) configuration mode.
Example
switch(config)# policy-map type quality-of-service PMAP-1
switch(config-pmap-PMAP-1)# class CMAP-1
switch(config-pmap-c-PMAP-1-CMAP-1)#class (policy-map (qos) Trident II)
The class command places the switch in the policy-map-class (QoS) configuration mode, which is a group change mode that modifies the specified class of the configuration mode policy map. The command adds the class to the policy map if it was not previously included in the policy map. All changes in a group change mode edit session are pending until the end of the session.
- The class map identifies a data stream through an ACL. Class maps are configured in class-map (qos) configuration mode.
- Set commands either modify a packets content (CoS or DSCP fields) or assigns it to a traffic class queue. Set commands are configured in policy-map-class (qos) configuration mode.
Data packets are managed by commands of the first class whose map matches the packets content.
The exit command returns the switch to the policy-map configuration mode. However, saving the policy-map-class changes also require an exit from the policy-map mode. This saves all the pending policy map and policy-map-class changes to running-config and returns the switch to the global configuration mode. The abort command discards pending changes, returning the switch to the global configuration mode.
The no class and default class commands remove the class assignment from the configuration mode policy map by deleting the corresponding class configuration from running-config.
Command Mode
Policy-Map (qos) Configuration accessed through policy-map type quality-of-service command.
Command Syntax
class class_name [PLACEMENT]
no class class_name [PLACEMENT]
default class class_name [PLACEMENT]
- class_name name of the class.
- PLACEMENT Specifies the map placement within the
list of class maps.
- no parameter Class is placed at the top of the list.
- insert-before existing_class Class is inserted in front of the specified class.
- set (policy-map-class (qos) Trident II)
- exit saves pending class changes and returns switch to policy-map (qos) configuration mode.
- abort discards pending class changes and returns switch to policy-map (qos) configuration mode.
- class-map type qos places switch in class-map (qos) configuration mode.
- policy-map type quality-of-service places switch in policy-map (qos) configuration mode.
Example
switch(config)# policy-map type quality-of-service PMAP-1
switch(config-pmap-PMAP-1)# class CMAP-1
switch(config-pmap-c-PMAP-1-CMAP-1)# class (policy-map (qos) Trident)
The class command places the switch in policy-map-class (qos) configuration mode, which is a group change mode that modifies the specified class of the configuration mode policy map. The command adds the class to the policy map if it was not previously included in the policy map. All changes in a group change mode edit session are pending until the end of the session.
- The class map identifies a data stream through an ACL. Class maps are configured in class-map (qos) configuration mode.
- Set commands either modify a packets content (CoS
or DSCP fields) or assigns it to a traffic class queue.
Set commands are configured in
policy-map-class (qos) configuration mode.
Data packets are managed by commands of the first class whose map matches the packets content.
The exit command returns the switch to policy-map configuration mode. However, saving policy-map-class changes also require an exit from policy-map mode. This saves all the pending policy map and policy-map-class changes to running-config and returns the switch to the global configuration mode. The abort command discards pending changes, returning the switch to the global configuration mode.
The no class and default class commands remove the class assignment from the configuration mode policy map by deleting the corresponding class configuration from running-config.
Command Mode
Policy-Map (qos) Configuration accessed through policy-map type quality-of-service command.
Command Syntax
class class_name [PLACEMENT]
no class class_name [PLACEMENT]
default class class_name [PLACEMENT]
- class_name name of the class.
- PLACEMENT Specifies the map placement within the
list of class maps.
- no parameter Class is placed at the top of the list.
- insert-before existing_class Class is inserted in front of the specified class.
- set (policy-map-class (qos) Trident)
- exit saves pending class changes and returns switch to policy-map (qos) configuration mode.
- abort discards pending class changes and returns switch to policy-map (qos) configuration mode.
- class-map type qos places switch in class-map (qos) configuration mode.
- policy-map type quality-of-service places switch in policy-map (qos) configuration mode.
Example
switch(config)# policy-map type quality-of-service PMAP-1
switch(config-pmap-PMAP-1)# class CMAP-1
switch(config-pmap-c-PMAP-1-CMAP-1)#class-map type copp
The class-map type copp command places the switch in Class-Map (control plane) configuration mode, which is a group change mode that modifies a control-plane dynamic class map. A dynamic class map is a data structure that uses Access Control Lists (ACLs) to define a data stream by specifying characteristics of data packets that comprise that stream. Control-plane policy maps use class maps to specify which control plane traffic is controlled by policy map criteria.
The exit command saves pending class map changes to running-config and returns the switch to the global configuration mode. Class map changes are also saved by entering a different configuration mode. The abort command discards pending changes and returns the switch to the global configuration mode.
The no class-map type copp and default class-map type copp commands delete the specified class map by removing the corresponding class-map type copp command and its associated configuration.
Command Mode
Global Configuration
Command Syntax
class-map type copp match-any class_name
no class-map type copp [match-any] class_name
default class-map type copp [match-any] class_name
Parameter
class_name Name of class map.Commands Available in Class-Map (Control Plane) Configuration Mode
match (class-map (control-plane) Trident)
Example
switch(config)# class-map type copp match-any CP-CMAP-1
switch(config-cmap-CP-CMAP-1)#class-map type pbr
The class-map type pbr command places the switch in the class-map (pbr) configuration mode for the specified class map, and creates the class map if one does not already exist. The class-map (PBR) configuration mode is a group change mode that modifies a class map for Policy-Based Routing (PBR). PBR class maps contain one or more match statements which filter incoming traffic using ACLs. PBRs can then use these class maps to set next-hop IP addresses for the traffic that matches them. (Classes without set commands translate to no action being performed on that class of packets.)
The exit command saves pending class map changes to running-config, then returns the switch to the global configuration mode. Class map changes are also saved by directly entering a different configuration mode. The abort command discards pending changes and returns the switch to the global configuration mode.
The no class-map type pbr and default class-map type pbr commands delete the specified class map by removing the corresponding class-map type pbr command and its associated configuration.
Command Mode
Global Configuration
Command Syntax
class-map type pbr match-any map_name
no class-map type pbr match-any map_name
default class-map type pbr match-any map_name
Parameter
map_name Name of class map.Example
switch(config)# class-map type pbrmatch-any MAP1
switch(config-cmap-MAP1)#class-map type qos
The class-map type qos command places the switch in the class-map (QoS) configuration mode, which is a group change mode that modifies a QoS dynamic class map. A dynamic class map is a data structure that uses Access Control Lists (ACLs) to define a data stream by specifying characteristics of data packets that comprise that stream. QoS policy maps use class maps to specify the traffic (to which the policy map is assigned) that is transformed by policy map criteria.
The exit command saves pending class map changes to running-config, then returns the switch to the global configuration mode. Class map changes are also saved by entering a different configuration mode. The abort command discards pending changes and returns the switch to the global configuration mode.
The no class-map type qos and default class-map type qos commands delete the specified class map by removing the corresponding class-map type qos command and its associated configuration. The class-map and class-map type qos commands are equivalent.
Command Mode
Global Configuration
Command Syntax
class-map type qos match-any class_name
no class-map type qos match-any class_name
default class-map type qos match-any class_name
Parameters
class_name Name of class map.
class-map map_name and class-map type qos map_name are identical commands.
Example
switch(config)# class-map type qos match-any MAP-1
switch(config-cmap-MAP-1)#clear policy-map counters
The clear policy-map command resets the specified policy map counters to zero. Policy map counters record the quantity of packets that are filtered by the ACLs that comprise a specified policy map.
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC
Command Syntax
clear policy-map INTERFACE_NAME counters MAP_NAME
- INTERFACE_NAME Interface for which command clears
table counters. Options include:
- interface control-plane Control plane.
- MAP_NAME Policy map for which command clears counters.
Options include:
- copp-system-policy Name of only policy map supported for the control plane.
feature pbr
Policy-Based Routing (PBR) is a feature that is applied on IPv4 or IPv6 routable ports, to preferentially route packets. Forwarding is based on a policy that is enforced at the ingress of the applied interface and overrides normal routing decisions. In addition to matches on regular ACLs, PBR policy-maps can also include “raw match” statements that look like a single entry of an ACL as a convenience for users.
Configuration Mode
For IP:
TCAM PBR profile set TTL configuration mode.
For IPv6:
TCAM feature PBR IP configuration mode.
Command Syntax
For IP:
feature pbr ip [copy]
no feature pbr ip [copy]
default feature pbr ip [copy]
For IPv6:
feature pbr ipv6 [copy | bank]
no feature pbr ipv6 [copy | bank]
default featue pbr ipv6 [copy | bank]
Parameters
For IP:
copy Copy a feature from a TCAM profile.
For IPv6:
- copyCopy a feature from a TCAM profile.
- bankTCAM banks to reserve.
-
In the following example, the PBR is configured on an IP routable port.
(config)# hardware tcam (config-tcam)# profile pbr-set-ttl copy default (config-tcam-profile-pbr-set-ttl)# feature pbr ip -
In the following example, the PBR is configured on an IPv6 routable port.
(config)# hardware tcam (config-tcam)# profile pbr-set-ttl copy default (config-tcam-profile-pbr-set-ttl)# feature pbr ip (config-tcam-feature-pbr-ip)# feature pbr ipv6
feature traffic-policy cpu
The feature traffic-policy cpu command configures the CPU traffic policy features for the IPv4 and IPv6 traffic in user-defined TCAM profile.
The no feature traffic-policy cpu and default feature traffic-policy cpu commands remove the CPU policy configurations from running-config.
Command Mode
Hardware TCAM
Command Syntax
feature traffic-policy cpu [ipv4 | ipv6]
no feature traffic-policy cpu [ipv4 | ipv6]
default feature traffic-policy cpu [ipv4 | ipv6]
- ipv4 CPU traffic policy for IPv4 traffic.
- ipv6 CPU traffic policy for IPv6 traffic.
Example
switch(config)# hardware tcam
switch(config-hw-tcam)# profile test
switch(config-hw-tcam-profile-test)# feature traffic-policy cpu ipv4feature traffic-policy port
The feature traffic-policy port command configures the port-related traffic policy features for the IPv4 and IPv6 traffic in user-defined TCAM profile.
The no feature traffic-policy port and default feature traffic-policy port commands remove the CPU policy configurations from running-config.
Command Mode
Hardware TCAM
Command Syntax
feature traffic-policy port [ipv4 | ipv6]
no feature traffic-policy port [ipv4 | ipv6]
default feature traffic-policy port [ipv4 | ipv6]
- ipv4 port traffic policy for IPv4 traffic.
- ipv6 port traffic policy for IPv6 traffic.
Example
switch(config)# hardware tcam
switch(config-hw-tcam)# profile test
switch(config-hw-tcam-profile-test)# feature traffic-policy port ipv4match (class-map (control-plane) Helix)
The match command assigns an ACL to the configuration mode class map. A class map can contain only one ACL. Class maps only use permit rules to filter data; deny rules are ignored. The command accepts IPv4 and IPv4 standard ACLs.
A class map is assigned to a policy map by the class (policy-map (control-plane) Helix) command.
The class map (control plane) configuration mode is a group change mode. Match statements are not saved to running-config until the edit session is completed by exiting the mode.
The no match and default match commands remove the match statement from the configuration mode class map by deleting the corresponding command from running-config.
Command Mode
Class-Map (control plane) configuration accessed through class-map type copp command.
Command Syntax
match ip access-group list_name
no match ip access-group list_name
default match ip access-group list_name
Parameters
list_name name of ACL assigned to class map.- class-map type copp places the switch in the class-map configuration mode.
- exit saves pending class map changes, then returns the switch to the global configuration mode.
- abort discards pending class map changes, then returns the switch to the global configuration mode.
- class (policy-map (control-plane) Helix) assigns a class map to a policy map.
Guidelines
Static class maps cannot be modified by this command.
Match statements are saved to running-config only upon exiting class-map (control plane) configuration mode.
Example
switch(config)# class-map type copp map_1
switch(config-cmap-map_1)# match ip access-group list_1
switch(config-cmap-map_1)# exit
switch(config)#match (class-map (control-plane) Trident II)
The match command assigns an ACL to the configuration mode class map. A class map can contain only one ACL. Class maps only use permit rules to filter data; deny rules are ignored. The command accepts IPv4 and IPv4 standard ACLs.
A class map is assigned to a policy map by the class (policy-map (control-plane) Trident II) command.
The class map (control plane) configuration mode is a group change mode. Match statements are not saved to running-config until the edit session is completed by exiting the mode.
The no match and default match commands remove the match statement from the configuration mode class map by deleting the corresponding command from running-config.
Command Mode
Class-Map (control plane) configuration accessed through class-map type copp command.
Command Syntax
list_name
list_name
list_name
Parameter
list_name name of ACL assigned to class map.- class-map type copp places the switch in the class-map configuration mode.
- exit saves pending class map changes, then returns the switch to the global configuration mode.
- abort discards pending class map changes, then returns the switch to the global configuration mode.
- class (policy-map (control-plane) Trident II) assigns a class map to a policy map.
Guidelines
Static class maps cannot be modified by this command.
Match statements are saved to running-config only upon exiting class-map (control plane) configuration mode.
Example
switch(config)# class-map type copp map_1
switch(config-cmap-map_1)# match ip access-group list_1
switch(config-cmap-map_1)# exit
switch(config)#match (class-map (control-plane) Trident)
The match command assigns an ACL to the configuration mode class map. A class map can contain only one ACL. Class maps only use permit rules to filter data; deny rules are ignored. The command accepts IPv4, IPv6, IPv4 standard, and IPv6 standard ACLs.
A class map is assigned to a policy map by the class (policy-map (control-plane) Trident) command.
Class map (control plane) configuration mode is a group change mode. Match statements are not saved to running-config until the edit session is completed by exiting the mode.
The no match and default match commands remove the match statement from the configuration mode class map by deleting the corresponding command from running-config.
Command Mode
Class-Map (control plane) configuration accessed through class-map type copp command
Command Syntax
match IP_VERSION access-group list_name
no match IP_VERSION access-group list_name
default match IP_VERSION access-group list_name
- IP_VERSION IP version of the specified ACL. Options
include:
- ipv4 IPv4.
- ipv6 IPv6.
- list_name name of ACL assigned to class map.
- class-map type copp places the switch in class-map configuration mode.
- exit saves pending class map changes, then returns the switch to the global configuration mode.
- abort discards pending class map changes, then returns the switch to the global configuration mode.
- class (policy-map (control-plane) Trident) assigns a class map to a policy map.
Guidelines
Static class maps cannot be modified by this command.
Match statements are saved to running-config only upon exiting class-map (control plane) configuration mode.
Example
switch(config)# class-map type copp map_1
switch(config-cmap-map_1)# match ip access-group list_1
switch(config-cmap-map_1)# exit
switch(config)#match (class-map (pbr))
The match command assigns ACLs to the configuration mode Policy-Based Routing (PBR) class map. The command accepts IPv4, IPv4 standard, IPv6 and IPv6 standard ACLs.
Class map (pbr) configuration mode is a group change mode. Match statements are not saved to running-config until the edit session is completed by exiting the mode.
The no match and default match commands remove the match statement from the configuration mode class map by deleting the corresponding command from running-config.
Command Mode
Class-map (pbr) configuration accessed through class-map type pbr command.
Command Syntax
[sequence_number] match [ip | ipv6] access-group list_name
no [sequence_number] match [ip | ipv6] access-group list_name
default [sequence_number] [ip | ipv6] access-group list_name
no [sequence_number]
default [sequence_number]
Parameters
- sequence_number Sequence number (1 to 4294967295) assigned to the rule. If no number is entered, the number is derived by adding 10 to the number of the class maps last numbered line. To increase the distance between existing entries, use the resequence command.
- list_name name of ACL assigned to class map.
- class-map type pbr places the switch in the class-map configuration mode.
- exit saves pending class map changes, then returns the switch to the global configuration mode.
- abort discards pending class map changes, then returns the switch to the global configuration mode.
- class (policy-map (pbr)) assigns a class map to a policy map.
Example
switch(config)# class-map type pbr map1
switch(config-cmap-map1)# match ip access-group list1
switch(config-cmap-map1)# exit
switch(config)#match (class-map (qos) FM6000)
The match command assigns an ACL to the configuration mode class map. A class map can contain only one ACL. Class maps only use permit rules to filter data; deny rules are ignored. The command accepts IPv4 and IPv4 standard ACLs.
The class map (qos) configuration mode is a group change mode. Match statements are not saved to running-config until the edit session is completed by exiting the mode.
The no match and default match commands remove the match statement from the configuration mode class map by deleting the corresponding command from running-config.
Command Mode
Class-map (qos) configuration accessed through class-map type qos command.
Command Syntax
match IP_VERSION access-group list_name
no match IP_VERSION access-group list_name
default match IP_VERSION access-group list_name
- IP_VERSION IP version of the specified ACL. Options
include:
- ipv4 IPv4.
- list_name name of ACL assigned to class map.
- class-map type qos places the switch in the class-map configuration mode.
- exit saves pending class map changes, then returns the switch to the global configuration mode.
- abort discards pending class map changes, then returns the switch to the global configuration mode.
- class (policy-map (qos) FM6000) assigns a class map to a policy map.
Example
switch(config)# class-map type qos map_1
switch(config-cmap-map_1)# match ip access-group list_1
switch(config-cmap-map_1)# exit
switch(config)#match (class-map (qos) Helix)
The match command assigns an ACL to the configuration mode class map. A class map can contain only one ACL. Class maps only use permit rules to filter data; deny rules are ignored. The command accepts IPv4, IPv4 standard, IPv6, and IPv6 standard ACLs.
the class map (QoS) configuration mode is a group change mode. Match statements are not saved to running-config until the edit session is completed by exiting the mode.
The no match and default match commands remove the match statement from the configuration mode class map by deleting the corresponding command from running-config.
Command Mode
Class-Map (QoS) configuration accessed through class-map type qos command.
Command Syntax
match IP_VERSION access-group list_name
no match IP_VERSION access-group list_name
default match IP_VERSION access-group list_name
- IP_VERSION IP version of the specified ACL. Options
include:
- ipv4 IPv4.
- ipv6 IPv6.
- list_name name of ACL assigned to class map.
- class-map type qos places the switch in the class-map configuration mode.
- exit saves pending class map changes, then returns the switch to the global configuration mode.
- abort discards pending class map changes, then returns the switch to the global configuration mode.
- class (policy-map (qos) Helix) assigns a class map to a policy map.
Example
switch(config)# class-map type qos map_1
switch(config-cmap-map_1)# match ip access-group list_1
switch(config-cmap-map_1)# exit
switch(config)#match (class-map (qos) Trident II)
The match command assigns an ACL to the configuration mode class map. A class map can contain only one ACL. Class maps only use permit rules to filter data; deny rules are ignored. The command accepts IPv4, IPv4 standard, IPv6, and IPv6 standard ACLs.
The class map (QoS) configuration mode is a group change mode. Match statements are not saved to running-config until the edit session is completed by exiting the mode.
The no match and default match commands remove the match statement from the configuration mode class map by deleting the corresponding command from running-config.
Command Mode
The class-map (qos) configuration accessed through class-map type qos command.
Command Syntax
IP_VERSION list_name
IP_VERSION list_name
IP_VERSION list_name
- IP_VERSION IP version of the specified ACL. Options
include:
- ipv4 IPv4.
- ipv6 IPv6.
- list_name name of ACL assigned to class map.
- class-map type qos places the switch in the class-map configuration mode.
- exit saves pending class map changes, then returns the switch to the global configuration mode.
- abort discards pending class map changes, then returns the switch to the global configuration mode.
- class (policy-map (qos) Trident) assigns a class map to a policy map.
Example
switch(config)# class-map type qos map_1
switch(config-cmap-map_1)# match ip access-group list_1
switch(config-cmap-map_1)# exit
switch(config)#match (class-map (qos) Trident)
The match command assigns an ACL to the configuration mode class map. A class map can contain only one ACL. Class maps only use permit rules to filter data; deny rules are ignored. The command accepts IPv4, IPv4 standard, IPv6, and IPv6 standard ACLs.
Class map (QoS) configuration mode is a group change mode. Match statements are not saved to running-config until the edit session is completed by exiting the mode.
The no match and default match commands remove the match statement from the configuration mode class map by deleting the corresponding command from running-config.
Command Mode
Class-Map (qos) configuration accessed through class-map type qos command.
Command Syntax
match IP_VERSION access-group list_name
no match IP_VERSION access-group list_name
default match IP_VERSION access-group list_name
- IP_VERSION IP version of the specified ACL. Options
include:
- ipv4 IPv4.
- ipv6 IPv6.
- list_name name of ACL assigned to class map.
- class-map type qos places the switch in the class-map configuration mode.
- exit saves pending class map changes, then returns the switch to the global configuration mode.
- abort discards pending class map changes, then returns the switch to the global configuration mode.
- class (policy-map (qos) Trident) assigns a class map to a policy map.
Example
switch(config)# class-map type qos map_1
switch(config-cmap-map_1)# match ip access-group list_1
switch(config-cmap-map_1)# exit
switch(config)#match (policy-map (pbr))
The match command creates a policy map clause entry that specifies one filtering condition. When a packet matches the filtering criteria, its next hop is set as specified. When a packets properties do not equal the statement parameters, the packet is evaluated against the next clause or class map in the policy map, as determined by sequence number. If all clauses fail to set a next hop for the packet, the packet is routed according to the FIB.
The no match and default match commands remove the match statement from the configuration mode policy map by deleting the corresponding command from running-config.
Command Mode
Policy-Map (pbr) Configuration accessed through policy-map type pbr command.
Command Syntax
[sequence_number] match ip SOURCE_ADDR DEST_ADDR [set nexthop [recursive] NH-addr_1 [NH-addr_2] ... [NH-addr_n]]
no match ip SOURCE_ADDR DEST_ADDR [set nexthop [recursive] NH-addr_1 [NH-addr_2] ... [NH-addr_n]]
default match match ip SOURCE_ADDR DEST_ADDR [set nexthop [recursive] NH-addr_1 [NH-addr_2] ... [NH-addr_n]]
no SEQ_NUM
default SEQ_NUM
- sequence_number Sequence number assigned to the rule. If no number is entered, the number is derived by adding 10 to the number of the policy maps last numbered line. To increase the distance between existing entries, use the resequence command.
- SOURCE_ADDR and DEST_ADDR
source and destination address filters. Options include:
- network_addr subnet address (CIDR or address-mask).
- any packets from or to all addresses are matched.
- host
ip_addr IP address (dotted decimal
notation).
Source and destination subnet addresses support discontiguous masks.
- recursive enables recursive next hop resolution.
- NH_addr IP address of next hop. If multiple addresses are entered, they are treated as an ECMP group.
- policy-map type pbr enters the policy-map (PBR) configuration mode.
- show policy-map type pbr displays the PBR policy maps.
Example
switch(config)# policy-map type pbr PMAP1
switch(config-pmap-PMAP1)# match ip 172.16.0.0/12 any set nexthop 192.163.3.5
switch(config-pmap-PMAP1)# exit
switch(config)#platform arad tcam counters feature
The platform arad tcam counters feature command enables incrementing PBR hardware counters corresponding to ACL. If counters for PBR are enabled, then counters for ACL will be automatically disabled in all cases. If counters for ACL are enabled, then counters for PBR will be automatically disabled in all cases.
The no platform arad tcam counters feature command disables PBR/ACL counters selection. The default platform arad tcam counters feature commands resets the default behavior.
Command Mode
Global Configuration
Command Syntax
platform arad tcam counters feature [OPTIONS]
no platform arad tcam counters feature [OPTIONS]
default platform arad tcam counters feature [OPTIONS]
Parameters
- pbr assign the TCAM counters feature PBR hardware counters.
- acl assign the TCAM counters feature ACL hardware counters.
- This command enables incrementing ACL hardware counters
selection.
switch(config)# platform arad tcam counters feature acl switch(config)# - This command disables incrementing ACL hardware counters
selection.
switch(config)# no platform arad tcam counters feature acl switch(config)#
policy-map type copp
The policy-map type copp command places the switch in the policy-map (control plane) configuration mode, which is a group change mode that modifies a control-plane policy map. A policy map is a data structure that consists of class maps that identify a specific data stream and specify bandwidth and shaping parameters that controls its transmission. Control plane policy maps are applied to the control plane to manage traffic.
The copp-system-policy policy map is supplied with the switch and is always applied to the control plane. The copp-system-policy is the only valid control plane policy map.
The exit command saves pending policy map changes to running-config and returns the switch to the global configuration mode. Policy map changes are also saved by entering a different configuration mode. The abort command discards pending changes, returning the switch to the global configuration mode.
The no policy-map type copp and default policy-map type copp commands delete the specified policy map by removing the corresponding policy-map type copp command and its associated configuration.
Command Mode
Global Configuration
Command Syntax
policy-map type copp copp-system-policy
no policy-map type copp copp-system-policy
default policy-map type copp copp-system-policy
The copp-system-policy is supplied with the switch and is the only valid control plane policy map.
Related Commands
class-map type copp enters the control-plane class-map configuration mode for modifying a control-plane dynamic class map.
Only Helix and Trident platform switches support dynamic classes for control plane policing.
Example
switch(config)# policy-map type copp copp-system-policy
switch(config-pmap-copp-system-policy)#policy-map type pbr
The policy-map type pbr command places the switch in policy-map (pbr) configuration mode, which is a group change mode that modifies a Policy-Based Routing (PBR) policy map. The command also creates the specified policy map if it does not already exist. A PBR policy map is a data structure that consists of class maps that identify specific packets and the next hops for those packets. Policy maps are applied to Ethernet or port channel interfaces to manage traffic.
The exit command saves pending policy map changes to running-config and returns the switch to the global configuration mode. Policy map changes are also saved by entering a different configuration mode. The abort command discards pending changes, returning the switch to the global configuration mode.
The no policy-map type pbr and default policy-map type pbr commands delete the specified policy map by removing the corresponding policy-map type pbr command and its associated configuration.
Command Mode
Global Configuration
Command Syntax
policy-map type pbr map_name
no policy-map type pbr map_name
default policy-map type pbr map_name
Parameter
map_name Name of policy map.Example
switch(config)# policy-map type pbr PMAP1
switch(config-pmap-PMAP1)#policy-map type quality-of-service
The policy-map type quality-of-service command places the switch in the policy-map (QoS) configuration mode, which is a group change mode that modifies a QoS policy map. A policy map is a data structure that consists of class maps that identify a specific data stream and shaping parameters that controls its transmission. Policy maps are applied to Ethernet or port channel interfaces to manage traffic.
The exit command saves pending policy map changes to running-config and returns the switch to the global configuration mode. Policy map changes are also saved by entering a different configuration mode. The abort command discards pending changes, returning the switch to the global configuration mode.
The no policy-map type quality-of-service and default policy-map type quality-of-service commands delete the specified policy map by removing the corresponding policy-map type quality-of-service command and its associated configuration. The policy-map and policy-map type quality-of-service commands are equivalent.
Command Mode
Global Configuration
Command Syntax
policy-map type quality-of-service map_name
no policy-map type quality-of-service map_name
default policy-map type quality-of-service map_name
Parameter
map_name Name of policy map.Conditions
policy-map map_name and policy-map type quality-of-service map_name are identical commands.
Example
switch(config)# policy-map PMAP-1
switch(config-pmap-PMAP-1)#policy-map type quality-of-service policer
The policy-map type quality-of-service policer copy command is used to copy an existing QoS policy map to the policy map policer.
The policy-map type quality-of-service policer drop counter command is used to enable drop counters for the QoS policy map policer.
The no policy-map type quality-of-service policer and default policy-map type quality-of-service policer commands delete the policy map policer by removing the corresponding policy-map type quality-of-service policer command and its associated configuration.
The no policy-map type quality-of-service policer drop counter and default policy-map type quality-of-service policer drop counter commands disable drop counters for the policy map policer.
Command Mode
Global Configuration
Command Syntax
policy-map type quality-of-service policer copy map_name
policy-map type quality-of-service policer drop counter
no policy-map type quality-of-service policer
default policy-map type quality-of-service policer
Parameter
map_name Name of policy map to copy.Examples
- This command copies the QoS policy map named
PMAP-1 to the policy map
policer.
switch(config)#policy-map type quality-of-service policer copy PMAP-1 switch(config-pmap-PMAP-1)# - This command enables drop counters for the QoS policy map
policer.
switch(config)#policy-map type quality-of-service policer drop counter switch(config)#
resequence (class-map (pbr))
The resequence command assigns sequence numbers to rules in the configuration mode class map. Command parameters specify the number of the first rule and the numeric interval between consecutive rules. Once changed, rule numbers persist unless changed again using the resequence command, but the interval used for numbering new rules reverts to 10 on the exiting class-map (pbr) configuration mode.
Maximum rule sequence number is 4294967295.
Command Mode
Class-Map (PBR) Configuration accessed through class-map type pbr command.
Command Syntax
resequence [start_num [inc_num]]
- start_num sequence number assigned to the first rule. Default is 10.
- inc_num numeric interval between consecutive rules. Default is 10.
Example
switch(config)# class-map type pbr match-any CMAP1
switch(config-cmap-CMAP1)# show active
class-map type pbr match-any CMAP1
10 match ip access-group group1
20 match ip access-group group2
30 match ip access-group group3
switch(config-cmap-CMAP1)# resequence 100 20
switch(config-cmap-CMAP1)# exit
switch(config)# class-map type pbr match-any CMAP1
switch(config-cmap-CMAP1)# show active
class-map type pbr match-any CMAP1
100 match ip access-group group1
120 match ip access-group group2
140 match ip access-group group3resequence (policy-map (pbr))
The resequence command assigns sequence numbers to rules in the configuration mode policy map. Command parameters specify the number of the first rule and the numeric interval between consecutive rules. Once changed, rule numbers persist unless changed again using the resequence command, but the interval used for numbering new rules reverts to 10 on the exiting policy-map (pbr) configuration mode.
Maximum rule sequence number is 4294967295.
Command Mode
Policy-Map (PBR) Configuration accessed through policy-map type pbr command
Command Syntax
resequence [start_num [inc_num]]
- start_num sequence number assigned to the first rule. Default is 10.
- inc_num numeric interval between consecutive rules. Default is 10.
Example
switch(config)# policy-map type pbr PMAP1
switch(config-pmap-PMAP1)# show active
policy-map type pbr PMAP1
10 class CMAP1
set nexthop 172.16.1.1
20 class CMAP2
set nexthop 172.16.2.2
30 class CMAP3
set nexthop 172.16.3.3
switch(config-pmap-PMAP1)# resequence 100 20
switch(config-pmap-PMAP1)# exit
switch(config)# policy-map type pbr PMAP1
switch(config-pmap-PMAP1)# show active
class-map type pbr PMAP1
100 class CMAP1
set nexthop 172.16.1.1
120 class CMAP2
set nexthop 172.16.2.2
140 class CMAP3
set nexthop 172.16.3.3
switch(config-pmap-PMAP1)#service-policy type pbr (Interface mode)
The service-policy pbr command applies the specified Policy-Based Routing (PBR) policy map to the configuration mode interface. A PBR policy map is a data structure that consists of class maps that identify specific packets and the next hops for those packets. Policy maps are applied to Ethernet or port channel interfaces to manage traffic. Only one service policy is supported per interface.
The no service-policy pbr and default service-policy pbr commands remove the service policy assignment from the configuration mode interface by deleting the corresponding service-policy pbr command from running-config.
Command Mode
Interface-Ethernet Configuration
Interface-Port-Channel Configuration
Interface-VLAN Configuration
Command Syntax
service-policy type pbr TRAFFIC_DIRECTION map_name
no service-policy type pbr TRAFFIC_DIRECTION map_name
default service-policy type pbr TRAFFIC_DIRECTION map_name
- TRAFFIC_DIRECTION IP address or peer group name.
Values include:
- input Policy map applies to inbound packet streams.
- map_name Name of policy map.
Guidelines
A policy map that is attached to a port channel interface takes precedence for member interfaces of the port channel over their individual interface Ethernet configuration. Members that are removed from a port channel revert to the policy map implementation specified by its interface Ethernet configuration.
Related Commands
policy-map type pbrExample
switch# config
switch(config)# interface ethernet 8
switch(config-if-Et8)# service-policy type pbr input PMAP1
switch(config-if-Et8)#service-policy type qos (Interface mode)
The service-policy command applies a specified policy map to the configuration mode interface. A policy map is a data structure that identifies data traffic through class maps, then specifies actions to classify the traffic (by setting the traffic class), mark the traffic (by setting the cos and dscp values), and police the traffic (by setting the police rate) through data packet field modifications.
The no service-policy and default service-policy commands remove the service policy assignment from the configuration mode interface by deleting the corresponding service-policy command from running-config.
Command Mode
Interface-Ethernet Configuration
Interface-Port-Channel Configuration
Interface-VLAN Configuration
Command Syntax
service-policy [type qos] TRAFFIC_DIRECTION map_name
no service-policy [type qos] TRAFFIC_DIRECTION map_name
default service-policy [type qos] TRAFFIC_DIRECTION map_name
- type qos Parameter has no functional effect.
- TRAFFIC_DIRECTION Direction of data stream to which
command applies. Options include:
- input Policy map applies to inbound packet streams.
- map_name Name of policy map.
Guidelines
A policy map that is attached to a port channel interface takes precedence for member interfaces of the port channel over their individual interface Ethernet configuration. Members that are removed from a port channel revert to the policy map implementation specified by its interface Ethernet configuration.
DCS-7500E and DCS-7280E limitations:
- A maximum of 31 QoS service policies per chip may be applied on L3 interfaces.
- Applying different QoS service policies to an SVI and its member interfaces causes unpredictable behavior.
- When an SVI on which QoS service policies are applied experiences partial failure due to limited hardware resources, a forwarding agent restart causes unpredictable behavior.
- Policy-map programming may fail when QoS service policies are applied on two SVIs if an event causes a member interface to switch membership from one to the other. To change the VLAN membership of an interface in this case, remove the interface from one VLAN before adding it to the other.
- Outgoing COS rewrite is not supported.
- QoS policy-map counters are not supported.
DCS-7010, DCS-7050, DCS-7050X, DCS-7250X, and DCS-7300X limitations:
- When the same policy map is applied to multiple SVIs, TCAM resources are not shared.
- A policy map applied to an SVI results in TCAM allocation on all chips whether SVI members are present or not.
- Applying different QoS service policies to an SVI and its member interfaces causes unpredictable behavior.
Related Commands
policy-map type quality-of-serviceExample
switch# config
switch(config)# interface ethernet 8
switch(config-if-Et8)# show active
switch(config-if-Et8)# service-policy input PMAP-1
switch(config-if-Et8)# show active
interface Ethernet8
service-policy type qos input PMAP-1
switch(config-if-Et8)#set (policy-map-class (qos)FM6000)
The set command specifies traffic resolution methods for traffic defined by its associated class map in its configuration mode policy map class. Three set statements are available for each class:
- cos Sets the Layer 2 class of service field.
- dscp Sets the differentiated services code point value in the type of service (ToS) byte.
- traffic-class Sets the traffic class queue for data packets.
Each type of set command can be assigned to a class, allowing for the simultaneous modification of both (cos, dscp) fields and assignment to a traffic class.
The no set and default set commands remove the specified data action from the class map by deleting the associated set command from running-config.
Command Mode
Policy-map-class (qos) configuration
accessed through class (policy-map (qos) FM6000) command.
Command Syntax
set QOS_TYPE value
no set QOS_TYPE
default set QOS_TYPE
- QOS_TYPE Specifies the data stream resolution
method. Valid options include:
- cos Layer 2 class of service field of outbound packet is modified.
- dscp Differentiated services code point value in the ToS byte is modified.
- traffic-class Data stream is assigned to a traffic class queue.
- value Specifies the data field value or traffic
class queue. Valid data range depends on
QOS_TYPE.
- QOS_TYPE is cos Value ranges from 0 to 7.
- QOS_TYPE is dscp Value ranges from 0 to 63.
- QOS_TYPE is traffic-class Value ranges from 0 to 7.
Example
switch(config)# policy-map type quality-of-service PMAP-1
switch(config-pmap-PMAP-1)# class CMAP-1
switch(config-pmap-c-PMAP-1-CMAP-1)# set cos 7
switch(config-pmap-c-PMAP-1-CMAP-1)# set traffic-class 4
switch(config-pmap-c-PMAP-1-CMAP-1)#set (policy-map-class (qos)Helix)
The set command specifies traffic resolution methods for traffic defined by its associated class map in its configuration mode policy map class. Three set statements are available for each class:
- cos Sets the Layer 2 class of service field.
- dscp Sets the differentiated services code point value in the type of service (ToS) byte.
- traffic-class Sets the traffic class queue for data packets.
Each type of set command can be assigned to a class, allowing for the simultaneous modification of both (cos, dscp) fields and assignment to a traffic class.
The no set and default set commands remove the specified data action from the class map by deleting the associated set command from running-config.
Command Mode
Policy-map-class (qos) configuration accessed through class (policy-map (qos) Helix) command.
Command Syntax
set QOS_TYPE value
no set QOS_TYPE
default set QOS_TYPE
- QOS_TYPE Specifies the data stream resolution
method. Valid options include:
- cos Layer 2 class of service field of outbound packet is modified.
- dscp Differentiated services code point value in the ToS byte is modified.
- traffic-class Data stream is assigned to a traffic class queue.
- value Specifies the data field value or traffic
class queue. Valid data range depends on QOS type.
- QOS_TYPE is cos Value ranges from 0 to 7.
- QOS_TYPE is dscp Value ranges from 0 to 63.
- QOS_TYPE is traffic-class Value ranges from 0 to 7.
Example
switch(config)# policy-map type quality-of-service PMAP-1
switch(config-pmap-PMAP-1)# class CMAP-1
switch(config-pmap-c-PMAP-1-CMAP-1)# set cos 7
switch(config-pmap-c-PMAP-1-CMAP-1)# set traffic-class 4
switch(config-pmap-c-PMAP-1-CMAP-1)#set (policy-map-class (qos)Trident II)
The set command specifies traffic resolution methods for traffic defined by its associated class map in its configuration mode policy map class. Three set statements are available for each class:
- cos Sets the Layer 2 class of service field.
- dscp Sets the differentiated services code point value in the type of service (ToS) byte.
- traffic-class Sets the traffic class queue for data packets.
Each type of set command can be assigned to a class, allowing for the simultaneous modification of both (cos, dscp) fields and assignment to a traffic class.
The no set and default set commands remove the specified data action from the class map by deleting the associated set command from running-config.
Command Mode
Policy-map-class (qos) configuration accessed through class (policy-map (qos) Trident) command.
Command Syntax
set QOS_TYPE value
no set QOS_TYPE
default set QOS_TYPE
- QOS_TYPE Specifies the data stream resolution
method. Valid options include:
- cos Layer 2 class of service field of outbound packet is modified.
- dscp Differentiated services code point value in the ToS byte is modified.
- traffic-class Data stream is assigned to a traffic class queue.
- value Specifies the data field value or traffic
class queue. Valid data range depends on QOS type.
- QOS_TYPE is cos Value ranges from 0 to 7.
- QOS_TYPE is dscp Value ranges from 0 to 63.
- QOS_TYPE is traffic-class Value ranges from 0 to 7.
Example
switch(config)# policy-map type quality-of-service PMAP-1
switch(config-pmap-PMAP-1)# class CMAP-1
switch(config-pmap-c-PMAP-1-CMAP-1)# set cos 7
switch(config-pmap-c-PMAP-1-CMAP-1)# set traffic-class 4
switch(config-pmap-c-PMAP-1-CMAP-1)#set (policy-map-class (qos)Trident)
The set command specifies traffic resolution methods for traffic defined by its associated class map in its configuration mode policy map class. Three set statements are available for each class:
- cos Sets the Layer 2 class of service field.
- dscp Sets the differentiated services code point value in the type of service (ToS) byte.
- traffic-class Sets the traffic class queue for data packets.
Each type of set command can be assigned to a class, allowing for the simultaneous modification of both (cos, dscp) fields and assignment to a traffic class.
The no set and default set commands remove the specified data action from the class map by deleting the associated set command from running-config.
Command Mode
Policy-map-class (qos) configuration accessed through class (policy-map (qos) Trident) command.
Command Syntax
set QOS_TYPE value
no set QOS_TYPE
default set QOS_TYPE
- QOS_TYPE Specifies the data stream resolution
method. Valid options include:
- cos Layer 2 class of service field of outbound packet is modified.
- dscp Differentiated services code point value in the ToS byte is modified.
- traffic-class Data stream is assigned to a traffic class queue.
- value Specifies the data field value or traffic
class queue. Valid data range depends on QOS type.
- QOS_TYPE is cos Value ranges from 0 to 7.
- QOS_TYPE is dscp Value ranges from 0 to 63.
- QOS_TYPE is traffic-class Value ranges from 0 to 7.
Example
switch(config)# policy-map type quality-of-service PMAP-1
switch(config-pmap-PMAP-1)# class CMAP-1
switch(config-pmap-c-PMAP-1-CMAP-1)# set cos 7
switch(config-pmap-c-PMAP-1-CMAP-1)# set traffic-class 4
switch(config-pmap-c-PMAP-1-CMAP-1)#set nexthop (policy-map-class pbr)
The set nexthop command specifies the next hop for traffic defined by its associated class map in its configuration mode policy map class.
The no set nexthop and default set nexthop commands remove the specified action from the class map by deleting the associated set nexthop command from running-config.
Command Mode
Policy-map-class (pbr) configuration accessed through class (policy-map (pbr)) command.
Command Syntax
set nexthop [recursive] NH-addr_1 [NH-addr_2] ... [NH-addr_n]
no set nexthop [recursive]
default set nexthop [recursive]
- recursive enables recursive next hop resolution.
- NH_addr IP address of next hop. If multiple addresses are entered, they are treated as an ECMP group.
Example
switch(config)# policy-map type pbr PMAP1
switch(config-pmap-PMAP1)# class CMAP1
switch(config-pmap-c-PMAP1-CMAP1)# set nexthop 192.168.5.3
switch(config-pmap-c-PMAP1-CMAP1)#set nexthop-group (policy-map-class(pbr) Arad)
The set nexthop-group command specifies a nexthop group as the next hop for traffic defined by its associated class map in its configuration mode policy map class.
The no set nexthop-group and default set nexthop-group commands remove the specified action from the class map by deleting the associated set nexthop-group command from running-config.
Command Mode
Policy-map-class (pbr) configuration accessed through class (policy-map (pbr)) command.
Command Syntax
set nexthop-group group_name
no set nexthop-group group_name
default set nexthop-group group_name
Parameters
group_name name of ECMP group to use as next hop.
Example
switch(config)# policy-map type pbr PMAP1
switch(config-pmap-PMAP1)# class CMAP1
switch(config-pmap-c-PMAP1-CMAP1)# set nexthop-group GROUP1
switch(config-pmap-c-PMAP1-CMAP1)#shape (policy-map-class (control-plane)Arad)
The shape command specifies the maximum bandwidth for traffic filtered by the configuration mode policy map class.
The no shape and default shape commands remove the maximum bandwidth restriction for the configuration mode class by deleting the corresponding bandwidth command from running-config.
Command Mode
Policy-map-class (control plane) configuration accessed through class (policy-map (control-plane) Arad)
Command Syntax
Parameter
kilobits Maximum data rate in kilobits per second. Value ranges from 1 to 10000000.
- class (policy-map (control-plane) Arad) places the switch in the policy-map-class (control plane) configuration mode.
- bandwidth (policy-map-class (control-plane) Arad) specifies the minimum bandwidth for traffic defined by its associated class map in its configuration mode policy map class.
Static Classes Default Shape
- copp-system-bgp 2500 copp-system-l3lpmoverflow 2500
- copp-system-bpdu 2500 copp-system-l3slowpath 2500
- copp-system-default 2500 copp-system-l3ttl1 2500
- copp-system-ipbroadcast 2500 copp-system-lacp 2500
- copp-system-ipmc 2500 copp-system-linklocal 2500
- copp-system-ipmcmiss 2500 copp-system-lldp 2500
- copp-system-ipunicast NO LIMIT copp-system-mlag 2500
- copp-system-l2broadcast 2500 copp-system-multicastsnoop 2500
- copp-system-l2unicast NO LIMIT copp-system-OspfIsis 2500
- copp-system-l3destmiss 2500 copp-system-sflow 2500
Example
switch(config)# policy-map type copp copp-system-policy
switch(config-pmap-copp-system-policy)# class copp-system-lldp
switch(config-pmap-c-copp-system-policy-copp-system-lldp)# shape kbps 2000
switch(config-pmap-c-copp-system-policy-copp-system-lldp)# exit
switch(config-pmap-copp-system-policy)# exit
switch(config)# show policy-map copp copp-system-policy
Service-policy input: copp-system-policy
Class-map: copp-system-lldp (match-any)
shape : 2000 kbps
bandwidth : 250 kbps
Out Packets : 0
Drop Packets : 0
switch(config)#shape (policy-map-class (control-plane)FM6000)
The shape command specifies the maximum bandwidth for traffic filtered by the configuration mode policy map class.
The no shape and default shape commands remove the maximum bandwidth restriction for the configuration mode class by deleting the corresponding bandwidth command from running-config.
Command Mode
Policy-map-class (control plane) configuration accessed through class (policy-map (control-plane) FM6000).
Command Syntax
shape pps packets
no shape
default shape
Parameters
packets Maximum data rate in packets per second. Value ranges from 1 to 100000.
- class (policy-map (control-plane) FM6000) places the switch in the policy-map-class (control plane) configuration mode.
- bandwidth (policy-map-class (control-plane) FM6000) specifies the minimum bandwidth for traffic defined by its associated class map in its configuration mode policy map class.
Static Classes Default Shape
- copp-system-arp 10000 copp-system-l3slowpath 10000
- copp-system-default 8000 copp-system-pim-ptp 10000
- copp-system-ipmcrsvd 10000 copp-system-ospf-isis 10000
- copp-system-ipmcmiss 10000 copp-system-selfip 5000
- copp-system-igmp 10000 copp-system-selfip-tc6to7 5000
- copp-system-l2rsvd 10000 copp-system-sflow 25000
Example
switch(config)# policy-map type copp copp-system-policy
switch(config-pmap-copp-system-policy)# class PMAP-1
switch(config-pmap-c-copp-system-policy-PMAP-1)# shape pps 5000
switch(config-pmap-c-copp-system-policy-PMAP-1)#shape (policy-map-class (control-plane)Helix)
The shape command specifies the maximum bandwidth for traffic filtered by the configuration mode policy map class.
The no shape and default shape commands remove the maximum bandwidth restriction for the configuration mode class by deleting the corresponding bandwidth command from running-config.
Command Mode
Policy-map-class (control plane) configuration accessed through class (policy-map (control-plane) Helix).
Command Syntax
shape pps packets
no shape
default shape
Parameters
packets Maximum data rate in packets per second. Value ranges from 1 to 100000.
Static Classes Default Shape
- copp-system-acllog 10000 copp-system-l3ttl1 10000
- copp-system-arp 10000 copp-system-lacp 5000
- copp-system-arpresolver 10000 copp-system-lldp 10000
- copp-system-bfd 10000 copp-system-mlag 5000
- copp-system-bgp 5000 copp-system-OspfIsis 10000
- copp-system-bpdu 5000 copp-system-selfip 5000
- copp-system-default 8000 copp-system-selfip-tc6to7 5000
- copp-system-glean 10000 copp-system-sflow 25024
- copp-system-igmp 10000 copp-system-tc3to5 10000
- copp-system-ipmcmiss 10000 copp-system-tc6to7 10000
- copp-system-ipmcrsvd 10000 copp-system-urm 10000
- copp-system-l3destmiss 10000 copp-system-vrrp 5000
- copp-system-l3slowpath 10000
- class (policy-map (control-plane) Helix) places the switch in the policy-map-class (control plane) configuration mode.
- bandwidth (policy-map-class (control-plane) Helix) specifies the minimum bandwidth for traffic defined by its associated class map in its configuration mode policy map class.
Example
switch(config)# policy-map type control-plan copp-system-policy
switch(config-pmap-copp-system-policy)# class copp-system-lldp
switch(config-pmap-c-copp-system-policy-copp-system-lldp)# shape pps 5000
switch(config-pmap-c-copp-system-policy-copp-system-lldp)# exit
switch(config-pmap-copp-system-policy)# exit
switch(config)# show policy-map copp copp-system-policy
Service-policy input: copp-system-policy
Class-map: copp-system-lldp (match-any)
shape : 5000 pps
bandwidth : 500 pps
Out Packets : 305961
Drop Packets : 0
switch(config)#shape (policy-map-class (control-plane)Petra)
The shape command specifies the maximum bandwidth for traffic filtered by the configuration mode policy map class.
The no shape and default shape commands remove the maximum bandwidth restriction for the configuration mode class by deleting the corresponding bandwidth command from running-config.
Command Mode
Policy-map-class (control plane) configuration accessed through class (policy-map (control-plane) Petra)
Command Syntax
shape kbps kilobits
no shape
default shape
Parameter
kilobits Maximum data rate in kilobits per second. Value ranges from 1 to 10000000.
- class (policy-map (control-plane) Petra) places the switch in policy-map-class (control plane) configuration mode.
- bandwidth (policy-map-class (control-plane) Petra) specifies the minimum bandwidth for traffic defined by its associated class map in its configuration mode policy map class.
Static Classes Default Shape
- copp-system-bpdu 2500 copp-system-l3destmiss 2500
- copp-system-default 2500 copp-system-l3slowpath 2500
- copp-system-igmp 2500 copp-system-l3ttl0 2500
- copp-system-ipbroadcast 2500 copp-system-l3ttl1 2500
- copp-system-ipmc 2500 copp-system-lacp 2500
- copp-system-ipmcmiss 2500 copp-system-lldp 2500
- copp-system-ipmcrsvd 2500 copp-system-unicast-arp 2500
- copp-system-ipunicast No Limit
Guidelines
Petra does not support all discrete rate values. When a specified discrete value is not supported, the switch converts the rate to the next highest discrete value that it supports. The show command displays the converted rate and not the user-configured rate.
Example
switch(config)# policy-map type copp copp-system-policy
switch(config-pmap-copp-system-policy)# class copp-system-lldp
switch(config-pmap-c-copp-system-policy-copp-system-lldp)# shape kbps 2000
switch(config-pmap-c-copp-system-policy-copp-system-lldp)# exit
switch(config-pmap-copp-system-policy)# exit
switch(config)# show policy-map copp copp-system-policy
Service-policy input: copp-system-policy
Class-map: copp-system-lldp (match-any)
shape : 2115 kbps
bandwidth : 325 kbps
Out Packets : 0
Drop Packets : 0
switch(config)#shape (policy-map-class (control-plane)Trident II)
The shape command specifies the maximum bandwidth for traffic filtered by the configuration mode policy map class.
The no shape and default shape commands remove the maximum bandwidth restriction for the configuration mode class by deleting the corresponding bandwidth command from running-config.
Command Mode
Policy-map-class (control plane) configuration accessed through class (policy-map (control-plane) Trident II).
Command Syntax
shape pps packets
no shape
default shape
Parameter
packets Maximum data rate in packets per second. Value ranges from 1 to 100000.
Static Classes Default Shape
- copp-system-acllog 10000 copp-system-l3slowpath 10000
- copp-system-arp 10000 copp-system-l3ttl1 10000
- copp-system-arpresolver 10000 copp-system-lacp 5000
- copp-system-bfd 10000 copp-system-lldp 10000
- copp-system-bgp 5000 copp-system-mlag 5000
- copp-system-bpdu 5000 copp-system-selfip 5000
- copp-system-default 8000 copp-system-selfip-tc6to7 5000
- copp-system-glean 10000 copp-system-sflow 25024
- copp-system-igmp 10000 copp-system-tc3to5 10000
- copp-system-ipmcmiss 10000 copp-system-tc6to7 10000
- copp-system-ipmcrsvd 10000 copp-system-urm 10000
- class (policy-map (control-plane) Trident II) places the switch in policy-map-class (control plane) configuration mode.
- bandwidth (policy-map-class (control-plane) Trident II) specifies the minimum bandwidth for traffic defined by its associated class map in its configuration mode policy map class.
Example
switch(config)# policy-map type control-plan copp-system-policy
switch(config-pmap-copp-system-policy)# class copp-system-lldp
switch(config-pmap-c-copp-system-policy-copp-system-lldp)# shape pps 5000
switch(config-pmap-c-copp-system-policy-copp-system-lldp)# exit
switch(config-pmap-copp-system-policy)# exit
switch(config)# show policy-map copp copp-system-policy
Service-policy input: copp-system-policy
Class-map: copp-system-lldp (match-any)
shape : 5000 pps
bandwidth : 500 pps
Out Packets : 305961
Drop Packets : 0
switch(config)#shape (policy-map-class (control-plane)Trident)
The shape command specifies the maximum bandwidth for traffic filtered by the configuration mode policy map class.
The no shape and default shape commands remove the maximum bandwidth restriction for the configuration mode class by deleting the corresponding bandwidth command from running-config.
Command Mode
Policy-map-class (control plane) configuration accessed through class (policy-map (control-plane) Trident).
Command Syntax
shape pps packets
no shape
default shape
Parameters
packets Maximum data rate in packets per second. Value ranges from 1 to 100000.
Static Classes Default Shape
- copp-system-arp 10000 copp-system-lldp 10000
- copp-system-arpresolver 10000 copp-system-l3destmiss 10000
- copp-system-bpdu 5000 copp-system-l3slowpath 10000
- copp-system-default 8000 copp-system-l3ttl1 10000
- copp-system-glean 10000 copp-system-selfip 5000
- copp-system-igmp 10000 copp-system-selfip-tc6to7 5000
- copp-system-ipmcmiss 10000 copp-system-sflow 25000
- copp-system-ipmcrsvd 10000 copp-system-tc3to5 10000
- copp-system-lacp 5000 copp-system-tc6to7 10000
- class (policy-map (control-plane) Trident) places the switch in the policy-map-class (control plane) configuration mode.
- bandwidth (policy-map-class (control-plane) Trident) specifies the minimum bandwidth for traffic defined by its associated class map in its configuration mode policy map class.
Example
switch(config)# policy-map type copp copp-system-policy
switch(config-pmap-copp-system-policy)# class PMAP-1
switch(config-pmap-c-copp-system-policy-PMAP-1)# shape pps 5000
switch(config-pmap-c-copp-system-policy-PMAP-1)
show class-map type control-plane
The show class-map command displays contents of available control-plane class maps. Control-plane class maps can be added to the copp-system-policy policy map. Control-plane class maps can be static class maps defined by the system or dynamic maps created in class-map configuration mode.
Dynamic class maps are composed of statements that match IPv4 access control lists. Static class maps are defined by the switch and cannot be altered.
Command Mode
EXEC
Command Syntax
show class-map type control-plane [MAP_NAME]
Parameters
- no parameter Command displays all control plane class maps.
- name_text Command displays specified control-plane class maps.
- show class-map command displays QoS class maps.
- show class-map type qos displays control plane class maps.
Example
switch# show class-map type control-plane
Class-map: CM-CP1 (match-any)
Match: ip access-group name LIST-CP1
Class-map: copp-system-acllog (match-any)
Class-map: copp-system-arp (match-any)
Class-map: copp-system-arpresolver (match-any)
Class-map: copp-system-bpdu (match-any)
Class-map: copp-system-glean (match-any)
Class-map: copp-system-igmp (match-any)
Class-map: copp-system-ipmcmiss (match-any)
Class-map: copp-system-ipmcrsvd (match-any)
Class-map: copp-system-l3destmiss (match-any)
Class-map: copp-system-l3slowpath (match-any)
Class-map: copp-system-l3ttl1 (match-any)
Class-map: copp-system-lacp (match-any)
Class-map: copp-system-lldp (match-any)
Class-map: copp-system-selfip (match-any)
Class-map: copp-system-selfip-tc6to7 (match-any)
Class-map: copp-system-sflow (match-any)
Class-map: copp-system-tc3to5 (match-any)
Class-map: copp-system-tc6to7 (match-any)
switch>
show class-map type pbr
The show class-map command displays contents of all available Policy-Based Routing (PBR) class maps, or of a specified PBR class map. PBR class maps are used by PBR policy maps. PBR class maps are dynamic maps that are created in class-map-configuration mode. Dynamic class maps are composed of statements that match IPv4 or IPv6 access control lists.
Command Mode
EXEC
Command Syntax
show class-map type pbr [map_name]
Parameters
map_name Name of class map displayed by the command. If no parameter is entered, command show all available PBR class maps.
Related Command
show policy-map type pbr displays PBR policy maps.
Example
switch# show class-map type pbr CMAP1
Class-map: CMAP1 (match-any)
Match: 10 ip access-group PBRgroup1
Match: 20 ip access-group PBRgroup2
Match: 30 ip access-group PBRgroup3
switch>show class-map type qos
The show class-mapcommand displays contents of all available QoS class maps. QoS class maps are used by QoS policy maps. QoS class maps are dynamic maps that are created in class-map configuration mode. Dynamic class maps are composed of statements that match IPv4 or IPv6 access control lists.
Command Mode
EXEC
Command Syntax
show class-map type qos [MAP_NAME]
Parameters
- no parameter Command displays all QoS class maps.
- name_text Command displays specified QoS class maps.
show class-map and show class-map type qos are identical commands.
Related Command
show class-map type control-plane displays control plane class maps.
Example
switch# show class-map type qos
Class-map: CM-Q1 (match-any)
Match: ipv6 access-group name LIST-1
Class-map: CM-Q2 (match-any)
Match: ip access-group name LIST-2show policy-map copp
The show policy-map copp command displays contents of the control-plane policy map. Control-plane policy maps are applied to the control plane, and copp-system-policy is the only supported policy map.
Command Mode
EXEC
Command Syntax
show policy-map copp copp-system-policy
Example
switch# show policy-map copp copp-system-policy
Service-policy input: copp-system-policy
Number of units programmed: 1
Hardware programming status: Successful
Class-map: copp-system-bpdu (match-any)
shape : 5000 pps
bandwidth : 5000 pps
Out Packets : 2
Drop Packets : 0
Class-map: copp-system-lacp (match-any)
shape : 5000 pps
bandwidth : 5000 pps
Out Packets : 0
Drop Packets : 0
switch>show policy-map interface type qos counters
The show policy-map interface command displays the quantity of packets that are filtered by ACLs applied to a interface.
Command Mode
EXEC
Command Syntax
show policy-map [INTERFACE_NAME][type qos][TRAFFIC] counters
- INTERFACE_NAME Filters policy map list by
interfaces. Options include:
- no parameter Displays data for all configured interfaces.
- interface ethernet e_range Ethernet ports for which command displays policy maps.
- interface port-channel p_range Port channels for which command displays policy maps.
- TRAFFIC Filters policy maps by the traffic they
manage. Options include:
- no parameter Policy maps that manage interfaces ingress traffic (same as input option).
- input Policy maps that manage interfaces ingress traffic.
Example
switch# show policy-map interface ethernet 7-8
Service-policy input: PMAP-1
Hardware programming status: Successful
Class-map: cmap-1 (match-any)
Match: ip access-group name LIST-2
set cos 6
Class-map: class-default (match-any)
Service-policy input: PMAP-2
Hardware programming status: Successful
Class-map: cmap-2 (match-any)
Match: ip access-group name LIST-2
set dscp 10
Class-map: class-default (match-any)show policy-map interface type qos
The show policy-map interface command displays contents of the policy maps applied to specified interfaces or to the control plane.
Command Mode
EXEC
Command Syntax
show policy-map interface INTERFACE_NAME [type qos] [TRAFFIC]
- INTERFACE_NAME Filters policy map list by
interfaces. Options include:
- ethernet e_range Ethernet ports for which command displays policy maps.
- port-channel p_range Port channels for which command displays policy maps.
- TRAFFIC Filters policy maps by the traffic they
manage. Options include:
- no parameter Policy maps that manage interfaces ingress traffic (same as input option).
- input Policy maps that manage interfaces ingress traffic.
Example
switch# show policy-map interface ethernet 7-8
Service-policy input: PMAP-1
Hardware programming status: Successful
Class-map: cmap-1 (match-any)
Match: ip access-group name LIST-2
set cos 6
Class-map: class-default (match-any)
Service-policy input: PMAP-2
Hardware programming status: Successful
Class-map: cmap-2 (match-any)
Match: ip access-group name LIST-2
set dscp 10
Class-map: class-default (match-any)show policy-map type copp
The show policy-map type copp command displays contents of control plane policy maps. Control-plane policy maps are applied to the control plane; copp-system-policy is the only supported policy map.
Command options filter the output to display contents of all policy maps, contents of a specified policy map, or contents of a single class map within a specified policy map.
Command Mode
EXEC
Command Syntax
show policy-map type copp copp-system-policy [CMAP_NAME]
Parameters
- no parameter Command displays all class maps in specified policy map.
- class_name Command displays specified class map.
Example
switch# show policy-map type copp copp-system-policy class copp-system-bpdu
Class-map: copp-system-bpdu (match-any)
shape : 5000 pps
bandwidth : 5000 ppsshow policy-map type pbr
The show policy-map pbr command displays contents of Policy-Based Routing (PBR) policy maps. PBR policy maps are applied to Ethernet interfaces, port channel interfaces or switch virtual interfaces (SVIs).
Command options filter the output to either display contents of all policy maps, contents of a specified policy map, or summary contents of all or a specified policy map.
Command Mode
EXEC
Command Syntax
show policy-map type pbr [PMAP_NAME][DATA_LEVEL]
- PMAP_NAME Name of policy map displayed by the
command.
- no parameter Command displays all policy maps.
- policy_map Command displays specified policy map.
- DATA_LEVEL Type of information the command displays.
Values include:
- no parameter Command displays all class maps in specified policy map.
- summary Command displays summary data for the specified policy map.
Example
switch# show policy-map type pbr
Service policy PMAP1
Configured on:
Applied on:
10: Class-map: CMAP1 (match-any)
Match: 10 ip access-group PBRgroup1
Match: 20 ip access-group PBRgroup2
Match: 30 ip access-group PBRgroup3
Configured actions: set nexthop 172.16.10.12
20: Class-map: CMAP2 (match-any)
Match: 10 ip access-group PBRgroup1
Match: 10 ip access-group PBRgroup4
Match: 20 ip access-group PBRgroup5
Configured actions: set nexthop 192.168.15.15show policy-map type qos counters
The show policy-map counters command displays the quantity of packets that are filtered by the ACLs that comprise a specified QoS policy map.
Command Mode
EXEC
Command Syntax
show policy-map type qos pmap_name [TRAFFIC] counters [INFO_LEVEL]
- pmap_name Name of policy map displayed by the command.
- TRAFFIC Filters policy maps by the traffic they
manage. Options include:
- no parameter Policy maps that manage interfaces ingress traffic (same as input option).
- input Policy maps that manage interfaces ingress traffic.
- INFO_LEVEL amount of information that is displayed.
Options include:
- no parameter displays summarized information about the policy map.
- detail displays detailed policy map information.
show policy-map type qos
The show policy-map qos command displays contents of QoS policy maps. QoS policy maps are applied to Ethernet or port channel interfaces.
Command options filter the output to either display contents of all policy maps, contents of a specified policy map, or contents of a single class map within a specified policy map.
Command Mode
EXEC
Command Syntax
show policy-map [type qos][PMAP_NAME [CMAP_NAME]]
- PMAP_NAME Name of policy map displayed by the
command.
- no parameter Command displays all policy maps.
- policy_map Command displays specified policy map.
- CMAP_NAME Name of class map displayed by the
command. This option is available only when the command includes a policy
map name.
- no parameter Command displays all class maps in specified policy map.
- class_name Command displays specified class map.
Example
switch# show policy-map type qos
Service-policy input: PMAP-1
Hardware programming status: Successful
Class-map: xeter (match-any)
Match: ip access-group name LIST-1
set cos 6
Class-map: class-default (match-any)
Service-policy PMAP-2
Class-map: class-default (match-any)show traffic-policy
The show traffic-policy command displays traffic policy information on the interface.
Command Mode
EXEC
Command Syntax
show traffic-policy NAME interface
show traffic-policy interface [DETAILS]
Parameters
- summary Display summary information about the
policy.
- errors Display all configured remote grantees, associated profile name and latest update.
- details Display all interfaces on which the policy has been configured.
-
This command displays the summary information configured on the switch interfaces.
switch(config-traffic-policies)# show traffic-policy interface summary Traffic policy samplePolicy Configured on interfaces: Ethernet1/1, Ethernet2/1, Ethernet3/1, ... Applied on interfaces for IPv4 traffic: Ethernet1/1, Ethernet2/1, Ethernet3/1, ... Applied on interfaces for IPv6 traffic: Total number of rules configured: 3 match SIMPLE ipv4 match ipv4-all-default ipv4 match ipv6-all-default ipv6 -
This command displays information about the traffic policy named samplePolicy.
switch(config-traffic-policies)# show traffic-policy samplePolicy interface Traffic policy samplePolicy Configured on interfaces: Ethernet1/1, Ethernet2/1, Ethernet3/1, ... Applied on interfaces for IPv4 traffic: Ethernet1/1, Ethernet2/1, Ethernet3/1, ... Applied on interfaces for IPv6 traffic: Total number of rules configured: 3 match SIMPLE ipv4 Source prefix: 192.0.2.0/24 198.51.100.0/24 Destination prefix: 203.0.113.0/24 Protocol: tcp Source port: 50-100 110-200 Actions: Drop match ipv4-all-default ipv4 match ipv6-all-default ipv6 -
This command displays all interfaces on which samplePolicy has been configured.
switch(config-traffic-policies)# show traffic-policy interface detail Traffic policy samplePolicy Configured on interfaces: Ethernet1/1, Ethernet2/1, Ethernet3/1, Ethernet4/1 Applied on interfaces for IPv4 traffic: Ethernet1/1, Ethernet2/1, Ethernet3/1, Ethernet4/1 Applied on interfaces for IPv6 traffic: Total number of rules configured: 3 match SIMPLE ipv4 Source prefix: 192.0.2.0/24 198.51.100.0/24 Destination prefix: 203.0.113.0/24 Protocol: tcp Source port: 50-100 110-200 Actions: Drop match ipv4-all-default ipv4 match ipv6-all-default ipv6 -
This command displays installation errors for a match statement. The example has no errors.
switch(config-traffic-policies)# show traffic-policy interface errors Traffic policy samplePolicy Failed on interface for IPv4 traffic: Failed on interface for IPv6 traffic:
