VM Tracer
Introducing VM Tracer
- Instantiated VMs with the network configuration, including VLANs and distributed or virtual switches.
- Provide server hardware IPMI data to the network manager.
VM Tracer also supports adaptive auto-segmentation, which automatically provisions and prunes VLANs from server-switched ports as VMs are instantiated and moved within the data center.
VM Tracer Description
- A Virtual Machine (VM) contains software that emulates a computer running on dedicated physical hardware. Multiple VMs share physical computer resources from a single physical device. The operating system controls each VM.
- A hypervisor, a Virtual Machine Manager (VMM), manages multiple operating systems running concurrently on a physical device.
VM Tracer tracks the activity of VMs controlled by hypervisors connected to the switch Ethernet or LAG ports. It supports vSphere versions 6.0– 7.0. The vSphere features include Distributed Virtual Switches (DVS) and VM movement among VMware servers (VMotion).
- ESX and ESXi - Hypervisors that run on VMware host server hardware.
- vCenter -A centralized tool that manages multiple servers running VMware hypervisors.
- NSX for vSphere® (NSX-V) - A network virtualization platform delivering networking and security.
Monitoring VLAN-based Configurations
vCenter manages ESX hosts and VMs through a central database. VM Tracer identifies interfaces connected to a specified ESX host and sends discovery packets (CDP or LLDP) on interfaces where VM Tracer is enabled. The ESX host updates the vCenter when it receives a discovery packet. VM Tracer reads this data from the vCenter through a SOAP (Simple Object Access Protocol) XML API to associate the ESX host to the connected switch ports. The following figure displays the network topology of this configuration.
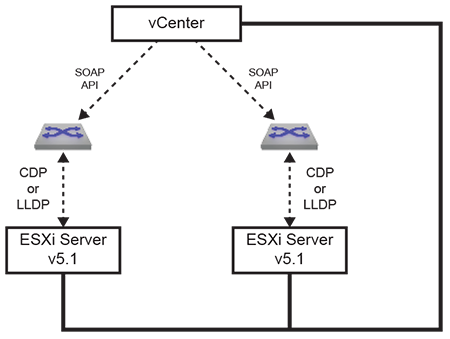
VM Tracer connects to a maximum of four vCenters through a SOAP XML API to discover VMs in the data centers managed by the vCenters. VM Tracer maintains a list of VMs in the data center and collects network-related information about each VM, including the number of Vnics (virtual network interface card), each Vnic MAC address, the connected switch, and the host on which it resides. VM Tracer also identifies the host NICs connected to the switch through the bridge MAC address and the interface port name. VM Tracer then searches for VMs on this host and connects to the vswitch or dvswitch with the uplink mapped to the connected NIC.
VM Tracer creates a VM Table for each connected interface that lists the active VMs, sorted by Vnic MAC address. Each VM entry includes the name, Vnic name, VLAN, switch name, datacenter name, and port group. The VM Table deletes the VM entry after removing the corresponding VM, moving the VM to a different host, or the Vnic no longer exists as part of the vswitch or dvswitch. The VM Table adds an entry after creating a VM or moving a VM to a host connected to the interface. VM Tracer monitors vCenter for VM management updates. If an interface goes down, the VM Table removes all VM entries for that interface.
Monitoring VXLAN-based Configurations
- VNI range
- VXLAN segment
- Multicast address range
- Network scope
The network scope specifies the virtual address space that the VXLAN segments span and the server group (cluster) collections within the segments, which in turn contain a collection of distributed virtual switches (DVS) from ESX hosts within the clusters.
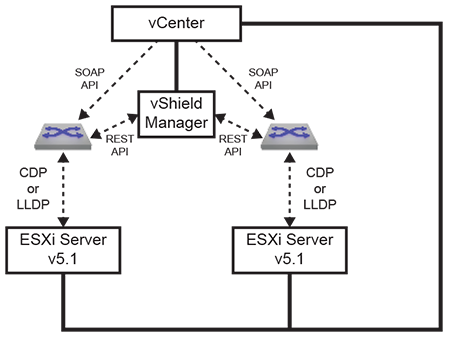
VM Tracer uses this information to build a network model. Communications with NSX-V require a single polling thread that detects network connectivity and constantly updates the local data model.
The following diagram displays the network topology of this configuration.
VM Tracer Configuration Procedures
- vmtracer configuration mode is a command mode for configuring VM Tracer monitoring sessions.
- VMtracer mode defines an interface state that sends discovery packets to attached vSwitches.
Configuring vCenter Monitoring Sessions
A VM Tracer session connects the switch to a vCenter server for downloading data about VMs and vSwitches managed by ESX hosts connected to the switch ports. The switch supports four VM Tracer sessions.
Place the switch in the vmtracer configuration mode to edit session parameters, including the vCenter location and dynamic VLAN usage. Changes take effect by exiting vmtracer configuration mode.
The vmtracer session command places the switch in the vmtracer configuration mode for a specified session. The command either creates a new session or loads an existing session for editing.
Example
switch(config)# vmtracer session system_1
switch(vmtracer-system_1)#
In vmtracer configuration mode, the url (vmtracer mode), username, and password commands specify the location and the account information that authenticates the switch. The URL parameter must reference a fully formed secure URL.
Example
switch(vmtracer-system_1)# url https://example.com/sdk
switch(vmtracer-system_1)# username a-switch_01
switch(vmtracer-system_1)# password abcde
switch(vmtracer-system_1)#Default session settings permit auto-segmentation, or the dynamic allocation and pruning of VLANs when creating, deleting, or moving a VM managed by the ESX host to a different host. The autovlan disable command prevents auto-segmentation, regardless of VM activity. The allowed-vlancommand specifies the available VLANs when adding or moving a VM. By default, all VLANs are allowed.
- This command disables auto-segmentation.
switch(vmtracer-system_1)# autovlan disable switch(vmtracer-system_1)# - These commands enable auto-segmentation and limit the list of allowed VLANs to VLAN 1-2000.
switch(vmtracer-system_1)# no autovlan disable switch(vmtracer-system_1)# allow-vlan 1-2000 switch(vmtracer-system_1)#
The exit command returns the switch to the global configuration mode and enables the VM Tracer session. The vmtracer configuration mode can be re-entered for this session to edit session parameters.
Example
switch(vmtracer-system_1)# exit
switch(config)#
The no vmtracer session command disables the session and removes it from running-config.
Example
switch(config)# no vmtracer session system_1
switch(config)#
Configuring vShield Monitoring Sessions
The switch must communicate with an NSX for vSphere® (NSX-V) to monitor VXLAN-based VMware configurations. The vmtracer-VXLAN configuration mode specifies the location and user account data that permits the switch to access an NSX-V within the configuration mode vmtracer session.
Place the switch in the vmtracer configuration mode to edit session parameters, including the vCenter location and dynamic VLAN usage. Changes take effect by exiting vmtracer mode.
Execute the vxlan command from the vmtracer mode for a specified session and places the switch in the vmtracer-VXLAN configuration mode for that session. Each VM Tracer session can be associated with one vShield instance.
Example
switch(config)# vmtracer session vnet-1
switch(config-vmtracer-vnet-1)# vxlan
switch(config-vmtracer-vnet-1-vxlan)#
In the vmtracer-vxlan configuration mode, the url, username (vmtracer-vxlan mode), and password (vmtracer-VXLAN mode) commands specify the vShield server location and the account information that authenticates the switch to the vShield server. The url parameter must reference a fully formed secure url, such as https://vcshield.democorp.com/sdk.
Example
switch(config-vmtracer-vnet-1-vxlan)# url https://vshieldserver.company1.org/sdk
switch(config-vmtracer-vnet-1-vxlan)# username a-shield_01
switch(config-vmtracer-vnet-1-vxlan)# password home
switch(config-vmtracer-vnet-1-vxlan)#
Enabling VMtracer Mode
VMtracer mode provides an interface setting that enables interfaces to send discovery packets to the connected vSwitch. The vmtracer command enables VMtracer mode on the configuration mode interface.
- These commands enable VMtracer mode on the interface Ethernet3.
switch(config)# interface Ethernet3 switch(config-if-Et3)# vmtracer vmware-esx switch(config-if-Et3)#
The no vmtracer command disables vmtracer mode on the configuration mode interface. - This command disables vmtracer mode on the interface ethernet 3.
switch(config-if-Et3)# no vmtracer vmware-esx switch(config-if-Et3)#
Displaying VM Tracer Data
Displaying Session Status
The show vmtracer session command displays information about the specified session.
Without the detail parameter, the command displays connection parameters and status for the vCenter associated to the specified session.
Example
switch# show vmtracer session system_1
vCenter URL https://vmware-vcenter1/sdk
username arista
password arista
Session Status Disconnected
With the detail parameter, the command displays connection status and data concerning messages the vCenter previously received from ESX hosts connected to the switch.
Example
switch# show vmtracer session system_1 detail
vCenter URL https://vmware-vcenter1/sdk
username arista
sessionState Connected
lastStateChange 19 days, 23:03:59 ago
lastMsgSent CheckForUpdatesMsg
timeOfLastMsg 19 days, 23:14:09 ago
resonseTimeForLastMsg 0.0
numSuccessfulMsg 43183
lastSuccessfulMsg CheckForUpdatesMsg
lastSuccessfulMsgTime 19 days, 23:14:19 ago
numFailedMsg 1076
lastFailedMsg CheckForUpdatesMsg
lastFailedMsgTime 19 days, 23:14:09 ago
lastErrorCode Error -1 fault: SOAP-ENV:Client [no subcode]
"End of file or no input: Operation interrupted or timed out after 600s send
or 600s receive delay"
Detail: [no detail]
CheckForUpdates:
Displaying VM Interfaces
The show vmtracer interface command displays the VM interfaces (Vnics) active on switch interfaces with vmtracer mode enabled. For each Vnic, the command displays the name of the attached VM, the adapter name, the VLAN, the VM power state, and the presence status of its MAC address in the switch MAC table.
This command displays the Vnics connected to all VM Tracer-enabled interfaces.
switch# show vmtracer interface
Ethernet8 : example.com
VM Name VM Adapter VLAN Status
esx3.aristanetworks.com vmk0 0 Up/Down
vspheremanagement Network adapter 1 0 Up/Down
Ethernet15 : example.om
VM Name VM Adapter VLAN Status
Openview Network adapter 1 123 Up/Down
VmTracerVm Network adapter 1 123 Down/Down
Ethernet23 : example.com
VM Name VM Adapter VLAN Status
Ethernet24 : example.com
VM Name VM Adapter VLAN Status
Displaying VMs
- This command displays the VMs connected to all VM Tracer-enabled interfaces.
switch# show vmtracer vm VM Name VM Adapter Interface VLAN Openview Network adapter 1 Et15 123 vspheremanagement Network adapter 1 Et8 0 VmTracerVm Network adapter 1 Et15 123 example.com vmk0 Et8 0 - This command displays connection data for the VMs connected to all VM Tracer-enabled interfaces.
switch# show vmtracer vm detail VM Name Openview intf : Et15 vnic : Network adapter 1 mac : 00:0c:29:ae:7e:90 portgroup : dvportGroup vlan : 123 switch : vds host : example.com
VM Tracer Commands
Global Configuration Commands
Interface Configuration (Ethernet and port channel) Commands
VMTracer Configuration Commands
VMTracer-VXLAN Configuration Commands
VM Tracer Display Commands
allowed-vlan
The allowed-vlan command specifies the VLANs that may be added when adding or moving a VM from the hypervisor connected to the session specified by the vmtracer mode. By default, all VLANs are allowed.
Command Mode
Vmtracer Configuration
Command Syntax
allowed-vlan [VLAN_LIST]
no allowed-vlan
default allowed-vlan vlan
Parameters
- v_range The list consists of the v_range VLANs.
- add v_range The v_range VLANs are added to the current VLAN list.
- all The list consists of all VLANs (1-4094).
- except v_range The list consists of all VLANs except for those specified by v_range.
- none The list of VLANs is empty.
- remove v_range The v_range VLANs are removed from the current VLAN list.
Related Command
vmtracer session vmtracer session places the switch in the vmtracer configuration mode.
- This command sets the list of allowed VLANs to 1 through 2000.
switch(vmtracer-system_1)# allow-vlan 1-2000 switch(vmtracer-system_1)# - This command adds VLANs to 2501 through 3000.
switch(vmtracer-system_1)# allow-vlan add 2051-3000 switch(vmtracer-system_1)#
autovlan disable
Default VM Tracer session settings enable auto provisioning, which allows the dynamic assignment and pruning of VLANs when creating, deleting, or moving a VM attached to the ESX connected to the switch to a different ESX host. The autovlan setting controls auto provisioning.
The autovlan disable command disables auto provisioning, which prevents the creation or deletion of VLANs regardless of VM activity. The allowed-vlan command specifies the VLANs that may be added when a VM is added or moved. By default, all VLANs are allowed.
The no autovlan disable command enables the creation and deletion of VLANs caused by VM activity. This is the default setting.
Command Mode
Vmtracer Configuration
Command Syntax
autovlan disable
no autovlan disable
default autovlan disable
Related Command
vmtracer session places the switch in the vmtracer configuration mode.
Example
switch(vmtracer-system_1)# autovlan disable
switch(vmtracer-system_1)#password
The password command specifies the token that authorizes the username to the vCenter associated with the VM Tracer mode session.
Command Mode
Vmtracer Configuration
Command Syntax
password [ENCRYPTION] [password]
- ENCRYPTION - Encryption level of the password.
- no parameter - The password in a clear-text string.
- 0 - The password in a clear-text string. Equivalent to no parameter.
- 7 the password is an encrypted string.
- password - Text that authenticates the username.
- password is a clear-text string if ENCRYPTION specifies clear text.
- password is an encrypted string if ENCRYPTION specifies an encrypted string.
Related Command
vmtracer session places the switch in the vmtracer configuration mode.
Example
switch(vmtracer-system_1)# url https://example.com/sdk
switch(vmtracer-system_1)# username a-switch_01
switch(vmtracer-system_1)# password abcde
switch(vmtracer-system_1)#password (vmtracer-VXLAN mode)
The password command specifies the token that authorizes the username on the NSX for vSphere® (NSX-V) server located at the URL configured for the configuration mode VM Tracer. The switch uses this account to access NSX-V information.
The password statement is replaced in running-config for the configuration mode interface by a subsequent password command. The statement is removed by deleting the NSX-V instance through a vxlan command in vmtracer configuration mode.
Command Mode
Vmtracer-VXLAN Configuration
Command Syntax
password [ENCRYPTION] password
- ENCRYPTION encryption level of the password.
- no parameterpassword is a clear-text string.
- 0 theis a clear-text string. Equivalent to no parameter.
- 7 the password is an encrypted string.
- password text that autorizes the username.
- password is a clear-text string if ENCRYPTION specifies clear text.
- password is an encrypted string if ENCRYPTION specifies an encrypted string.
Related Commands
vxlan places the switch in the vmtracer-vxlan configuration mode.
Example
switch(config)# vmtracer session vnet-1
switch(config-vmtracer-vnet-1)# vxlan
switch(config-vmtracer-vnet-1-vxlan)# url https://example.com/sdk
switch(config-vmtracer-vnet-1-vxlan)# username admin
switch(config-vmtracer-vnet-1-vxlan)# password 5678
switch(config-vmtracer-vnet-1-vxlan)# exit
switch(config-vmtracer-vnet-1)# show active
vmtracer session vnet-1
allowed-vlan 1-4094
vxlan
url https://example.com/sdk
username admin
password 7 s2Xq4GSBlYU=
switch(config-vmtracer-vnet-1)#show vmtracer all
The show vmtracer all command displays VM Tracer data for all switches with the vSphere scope.
Command Mode
EXEC
Command Syntax
show vmtracer all
Example
switch> show vmtracer all
Switch : a109(10.10.30.109)
Ethernet49 : 10.102.28.3/10G
VM Name VM Adapter VLAN Status State
ABCD Network adapter 2 native Up/-- --
Switch : a164(10.10.30.(172.22.30.164)
Ethernet49 : 10.102.28.3/10G Storage Network/dvUplink1
VM Name VM Adapter VLAN Status State
WXYZ Network adapter 2 native Up/-- --
switch>show vmtracer interface
The show vmtracer interface command displays the VM interfaces (Vnics) active on the VM Tracer enabled interface. For each Vnic, the command displays the name of the attached VM, the adapter name, its VLAN, the VM power state, and the presence status of its MAC address in the switch MAC table.
Command Mode
EXEC
Command Syntax
show vmtracer interface [INT_NAME] [INFO_LEVEL]
- INT_NAME the interfaces to be configured. Values include:
- no parameter command returns information for all interfaces.
- ethernet e_range Ethernet interface range.
- port-channel p_range port channel interface range.
Valid e_range and p_range formats include number, number range, or comma-delimited list of numbers and ranges.
- INFO_LEVEL specifies information that the command returns.
- no parameter connection parameters and status for VM associated to specified sessions.
- detail connection status and data concerning messages the VM.
- host name of the connected host.
- This command displays the Vnics connected to all VM Tracer enabled interfaces.
switch > show vmtracer interface Ethernet8 : example.com VM Name VM Adapter VLAN Status esx3.aristanetworks.com vmk0 0 Up/Down vspheremanagement Network adapter 1 0 Up/Down Ethernet15 : example.com VM Name VM Adapter VLAN Status Openview Network adapter 1 123 Up/Down VmTracerVm Network adapter 1 123 Down/Down Ethernet23 : example.com VM Name VM Adapter VLAN Status switch> - This command displays the Vnics connected to the interface Ethernet8.
switch> show vmtracer interface Ethernet8 Ethernet8 : example.com VM Name VM Adapter VLAN Status example.com vmk0 0 Up/Down vspheremanagement Network adapter 1 0 Up/Down switch>
show vmtracer session
The show vmtracer session command displays vCenter and vShield connection information for a specified VM Tracer session.
Command Mode
EXEC
Command Syntax
show vmtracer session [SESSION_LIST]
Parameters
- no parameter all configured VM Tracer sessions.
- session_name name of one VM Tracer session.
Example
switch> show vmtracer session abcde
Session abcde
vCenter URL https://example.com/sdk
username Administrator
autovlan enabled
allowed-vlans 1-4094
sessionState Connected
VShield URL https:/vmware-vshield5.1.xyz.abcde.com
username admin
sessionState Connected
switch>show vmtracer session vcenter
The show vmtracer session vcenter command displays vCenter information for a specified VM Tracer session.
Command Mode
EXEC
Command Syntax
show vmtracer session session_name vcenter [INFO_LEVEL]
- session_name VM Tracer sessions for which the command returns information.
- INFO_LEVEL specifies information that the command returns.
- no parameter displays connection and status information for the specified vCenter.
- detail displays connection, status, and history information for the specified vCenter.
- This command displays connection parameters for the vCenter associated to the abcde session.
switch> show vmtracer session abcde vcenter Session abcde vCenter URL https://vmware-vcenter5.1/sdk username Administrator autovlan enabled allowed-vlans 1-4094 sessionState Connected switch> - This command displays connection parameters and history details from the vCenter associated to the abcde session.
switch> show vmtracer session abcde vcenter detail Session abcde vCenter URL https://vmware-vcenter5.1/sdk username Administrator autovlan enabled allowed-vlans 1-4094 SessionState Connected lastStateChange 2:46:50 ago lastMsgSent Query network hint message timeOfLastMsg 0:00:20 ago responseTimeForLastMsg 0.000102301000479 numSuccessfulMsg 998 lastSuccessfulMsg Query network hint message lastSuccessfulMsgTime 0:00:20 ago numFailedMsg 0 lastFailedMsg -- lastFailedMsgTime never lastErrorCode -- switch>
show vmtracer session vsm
The show vmtracer session vsm command displays NSX-V information for a specified VM Tracer session.
Command Mode
EXEC
Command Syntax
show vmtracer session session_name vsm [INFO_LEVEL]
- session_name VM Tracer sessions for which the command returns information.
- INFO_LEVEL specifies information that the command returns.
- no parameter connection and status information for the specified NSX-V.
- detail connection, status, and history information for the specified NSX-V.
- This command displays connection parameters for the NSX-V associated to the abcde session.
switch> show vmtracer session abcde vsm Session abcde VShield URL https://example.com/sdk username admin sessionState Connected switch> - This command displays connection parameters and history details from the vShield Manager associated to the abcde session.
switch> show vmtracer session abcde vsm detail Session abcde VShield URL https://vmware-vshield5.1/ username admin SessionState Connected LaststateChange 19 days, 23:14:19 ago LastMsgSent /api/2.0/vdn/scopes timeOfLastMsg 1 days, 13:22:09 ago responseTimeForLastMsg 0.3 sec numSuccessfulMsg 3649 lastSuccessfulMsg /api/2.0/vdn/scopes lastSuccessfulMsgTime 0:00:00 ago numFailedMsg 1 lastFailedMsg /api/2.0/vdn/config/segments lastFailedMsgTime 10 days, 1:15:29 ago lastErrorCode CURLE_COULDNT_RESOLVE_HOST - Couldn't resolve host The given remote host was not resolved. switch>
show vmtracer vm
The show vmtracer vm command displays VMs interfaces (Vnics) accessible to VM Tracer enabled interfaces. For each active VM, the command displays the name of the VM, its adapter, and the hypervisor to which it connects.
Command Mode
EXEC
Command Syntax
show vmtracer [INT_NAME] vm [VM_LIST]
- INT_NAME the interfaces name Values include:
- no parameter command returns information for all interfaces.
- interface ethernet e_range Ethernet interface range.
- interface port-channel p_range port channel interface range.
Valid e_range and p_range formats include a number, number range, or comma-delimited list of numbers and ranges.
- VM_LIST The virtual machines for which the command displays information. Options include:
- no parameter command returns information for all present VMs.
- vm_name command returns information only for specified VM.
Related Command
The show vmtracer vm detail command displays connection information for one or more specified VMs.
Example
switch> show vmtracer vm
VM Name Esx Host Interface VLAN Status
vCenter1 172.22.28.8 Po45 native Down/Down
vCenter2 172.22.28.8 Po45 native Up/Up
vCenter3 172.22.28.8 Po45 11 Down/Down
vCenter4 172.22.28.8 Po45 native Down/Down
VMKernel Po43 native Up/Up
demo vcenter 5 clone Po43 native Up/Up
switch>show vmtracer vm detail
The show vmtracer vm detail command displays connection data for VMs interfaces (Vnics) accessible to VM Tracer enabled interfaces.
Command Mode
EXEC
Command Syntax
show vmtracer vm [VM_LIST] detail
Parameters
- no parameter command returns information for all present VMs.
- vm_name command returns information only for specified VM.
- This command displays connection data for the VMs connected to all VM Tracer enabled interfaces.
switch# show vmtracer vm vmcenter1 VM Name vCenter1 Server App Interface : Po45 vNIC : Network adapter 1 MAC : 00:31:22:8e:b8:41 portgroup : VM Network VLAN : native Switch : Switch2 Status : Down/Down Host : 10.22.18.28 Data Center : vcenter-5 switch> - This command displays connection data for the VMs connected to all VM Tracer enabled interfaces.
switch> show vmtracer vm detail VM Name vCenter1 Server App Interface : Po45 vNIC : Network adapter 1 MAC : 00:31:22:8e:b8:41 portgroup : VM Network VLAN : native Switch : Switch2 Status : Down/Down Host : 10.22.18.28 Data Center : vcenter-5 VM Name vCenter2 Server App Interface : Po45 vNIC : vmk0 MAC : 00:33:23:3c:e1:4e portgroup : Management Network VLAN : native switch>
show vmtracer vnic counters
The show vmtracer interface vnic counters command displays input and output packet counts for VM interfaces (Vnics) active on the specified interface or VM.
Command Mode
EXEC
Command Syntax
show vmtracer [ENTITY] vnic counters
Parameters
- no parameter command returns information for all active VMs.
- interface ethernet e_range Ethernet interface range.
- interface port-channel p_range port channel interface range.
- vm vm_name command returns information for specified VM.
Valid e_range and p_range formats include a number, number range, or comma-delimited list of numbers and ranges.
Example
switch> show vmtracer interface ethernet 24 vnic counters
Physical Intf: Ethernet24
Host: 10.17.28.8/site1/dvUplink1
VM Name vNic Input Pkt/Byte/% Output Pkt/Byte/%
vCenter1 Network adapter 2 2550/ 187175/ 0.6 6/ 360/ 0.0
vCenter2 Network adapter 2 418615/ 30678024/ 99.4 1904439/ 1145654613/100.0
Summary 421165/ 30865199/100.0 1904445/ 1145654973/100.0
switch>show vmtracer vxlan segment
The show vmtracer vxlan segment command displays information about the VXLAN segments that are managed by the connected NSX for vSphere® (NSX-V).
Command Mode
EXEC
Command Syntax
show vmtracer segment ENTITY
Parameters
- no parameter displays information for VXLAN segments.
- pool displays resource pools available to segments.
- pool pool_name displays connection information about the specified pool.
- range displays the VNI range of the managed segments.
- This command displays the VXLAN segments managed by the NSX-V.
switch> show vmtracer vxlan segment Name VNI Multicast IP Network Scope ------------------------------------------------------------ Eng Wire 5002 237.0.0.1 abcde HR Wire 5000 237.0.0.2 abcde switch> - This command displays the resource pools available to the VXLANs.
switch> show vmtracer vxlan segment pool Name Description Segments ------------------------------------------------------------------------ abcde Spans Cluster 1 and Cluster 2 Eng Wire, HR Wire switch> - This command displays connection and packet information for the abcde pool.
switch> show vmtracer vxlan segment pool abcde Name: abcde Description: Spans Cluster 1 and Cluster 2 Segments: Eng Wire, HR Wire VXLAN Segment Cluster Host VTEP IP DVS VLAN MTU Eng Wire Cluster2 test2.example.com 10.168.200.1/24 dvs-test2 200 1600 Eng Wire Cluster1 test2.example.com 10.168.100.1/24 dvs-test1 100 1600 HR Wire Cluster1 test2.example.com 10.168.100.1/24 dvs-test1 100 1600 HR Wire Cluster2 test2.example.com 10.168.200.1/24 dvs-test2 200 1600 switch> - This command displays the VNI range of the VXLAN segments.
switch> show vmtracer vxlan segment range VNI Range Multicast IP Range -------------------------------------------- 5000 - 5024 237.0.0.1 - 237.0.0.117 Name VNI Multicast IP Network Scope ----------------------------------------------------------- HR Wire 5002 237.0.0.1 abcde Eng Wire 5000 237.0.0.2 abcde switch>
show vmtracer vxlan vm
The show vmtracer vxlan vm command displays the VXLAN segments, their VTEP IP numbers, and their VM endpoints that are managed by the connected NSX for vSphere® (NSX-V).
Command Mode
EXEC
Command Syntax
show vmtracer vxlan vm
Example
switch> show vmtracer vxlan vm
VXLAN Segment VTEP IP VLAN VMs
Eng Wire 192.168.200.1/24 200 Eng VM3, Eng VM2
Eng Wire 192.168.100.1/24 100 Eng VM1
HR Wire 192.168.100.1/24 100 HR VM2, HR VM1
HR Wire 192.168.200.1/24 200 --
switch>source-interface
The source-interface command allows you to connect to a remote vCenter endpoint by using the primary address of the interface as the source IP address. If the interface is not specified, the source IP address is determined by the routing table.
The no source-interface and default source-interface commands restore default behavior by removing the source-interface command from the running-config.
Command Mode
Vmtracer Configuration
Command Syntax
source-interface [INTERFACE_NAME]
no source-interface
default source-interface
Parameters
- Ethernet e_num specifies the Ethernet interface number.
- Loopback l_num specifies the loopback interface number. Value ranges from 0 to 2100.
- Management m_num specifies the management interface number. The values are 1 or 2.
- port-channel {lag_num | lag_num.sub_num} specifies the port-channel interface number. Value of interface ranges from 1 to 2000. Value of sub-interface ranges from 1 to 4094.
- Tunnel tunnel_num specifies the tunnel interface number. Value ranges from 1 to 255.
- UnconnectedEthernet port_num specifies the unconnected Ethernet port number. Value ranges from 1 to 8.
- VLAN vlan_num specifies the VLAN interface number. Value ranges from 1 to 4094.
Related Commands
The vmtracer session command places the switch in the vmtracer configuration mode.
- This command configures VM Tracer to use interface Ethernet 17 to derive the source address for session packets.
switch(config)# vmtracer session system_1 switch(config-vmtracer-session-system_1)# source-interface Ethernet 17 switch(config-vmtracer-session-system_1)# - This command configures interface Loopback 0 for VM Tracer session.
switch(config)# vmtracer session system_1 switch(config-vmtracer-session-system_1)# source-interface Loopback 0 switch(config-vmtracer-session-system_1)# - This command configures interface management 1 for VM Tracer session.
switch(config)# vmtracer session system_1 switch(config-vmtracer-session-system_1)# source-interface management 1 switch(config-vmtracer-session-system_1)# - This command configures port-channel 10 for VM Tracer session.
switch(config)# vmtracer session system_1 switch(config-vmtracer-session-system_1)# source-interface port-channel 10 switch(config-vmtracer-session-system_1)# - This command configures interface tunnel 25 for VM Tracer session.
switch(config)# vmtracer session system_1 switch(config-vmtracer-session-system_1)# source-interface tunnel 25 switch(config-vmtracer-session-system_1)# - This command configures unconnected interface Ethernet 1 for VM Tracer session.
switch(config)# vmtracer session system_1 switch(config-vmtracer-session-system_1)# source-interface unconnected Ethernet 1 switch(config-vmtracer-session-system_1)# - This command configures interface vlan 25 for VM Tracer session.
switch(config)# vmtracer session system_1 switch(config-vmtracer-session-system_1)# source-interface vlan 25 switch(config-vmtracer-session-system_1)#
url (vmtracer mode)
The url command specifies the vCenter server location that is monitored by the session being edited by the current vmtracer mode. The command must reference a fully formed secure url.
Command Mode
Vmtracer Configuration
Command Syntax
url url_name
Parameter
url_name location of the vCenter server. Valid formats include IP address (dotted decimal notation) and fully qualified domain name.
Related Commands
The vmtracer session command places the switch in the vmtracer configuration mode.
Example
switch(vmtracer-system_1)# url https://example.com/sdk
switch(vmtracer-system_1)#url
The url command specifies the NSX for vSphere® (NSX-V) server location monitored for VXLAN information by the configuration mode VM Tracer session. The command must reference a fully formed secure URL.
The url statement is replaced in running-config for the configuration mode session by a subsequent url command. The statement is removed by deleting the NSX-V instance through a vxlan command in vmtracer configuration mode.
Command Mode
Vmtracer-VXLAN Configuration
Command Syntax
url url_name
Parameter
url_name location of the NSX-V server. Valid formats include IP address (dotted decimal notation) and fully qualified domain name.
Related Commands
The vxlan command places the switch in the vmtracer-vxlan configuration mode.
Example
switch(config)# vmtracer session vnet-1
switch(config-vmtracer-vnet-1)# vxlan
switch(config-vmtracer-vnet-1-vxlan)# url https://example.com/sdk
switch(config-vmtracer-vnet-1-vxlan)# exit
switch(config-vmtracer-vnet-1)# show active
vmtracer session vnet-1
allowed-vlan 1-4094
vxlan
url https://example.com/sdk
switch(config-vmtracer-vnet-1)#username
The username command identifies the switch account name on the vCenter server. The switch uses this user name to access vCenter information.
Command Mode
Vmtracer Configuration
Command Syntax
username name_string
Parameter
name_string vCenter account user name. Parameter must match the user name configured on the vCenter.
Related Commands
The vmtracer session command places the switch in the vmtracer configuration mode.
Example
switch(vmtracer-system_1)# username a-switch_01
switch(vmtracer-system_1)#username (vmtracer-vxlan mode)
The username command identifies the switch’s account name on the NSX for vSphere® (NSX-V) server located at the URL configured for the configuration mode VM Tracer. The switch uses this user name to access NSX-V information.
The username statement is replaced in running-config for the configuration mode interface by a subsequent username command. The statement is removed by deleting the NSX-V instance through a vxlan command in the vmtracer configuration mode.
Command Mode
Vmtracer-VXLAN Configuration
Command Syntax
username name_string
Parameter
name_string NSX-V account user name. Parameter must match a user name configured on the NSX-V.
Related Commands
The vxlan command places the switch in the vmtracer-vxlan configuration mode.
Example
switch(config)# vmtracer session vnet-1
switch(config-vmtracer-vnet-1)# vxlan
switch(config-vmtracer-vnet-1-vxlan)# url https://example.com/sdk
switch(config-vmtracer-vnet-1-vxlan)# username admin
switch(config-vmtracer-vnet-1-vxlan)# exit
switch(config-vmtracer-vnet-1)# show active
vmtracer session vnet-1
allowed-vlan 1-4094
vxlan
url https://example.com/sdk
username admin
switch(config-vmtracer-vnet-1)#vmtracer
The vmtracer command enables vmtracer mode on the configuration mode interface. Interfaces with vmtracer mode enabled send discovery packets to the connected vSwitch.
The no vmtracer and default vmtracer commands disable vmtracer mode on the configuration mode interface by removing the corresponding vmtracer command from running-config.
Command Mode
Interface-Ethernet Configuration Interface-port-channel Configuration
Command Syntax
vmtracer HOST_TYPE
no vmtracer HOST_TYPE
default vmtracer HOST_TYPE
Parameters
- vmware-esx - ESX or ESXI hypervisor (VMware).
- These commands enable the vmtracer mode on the interface Ethernet 3.
switch(config)# interface Ethernet 3 switch(config-if-Et3)# vmtracer vmware-esx switch(config-if-Et3)# - This command disables the vmtracer mode on the interface Ethernet 3.
switch(config-if-Et3)# no vmtracer vmware-esx switch(config-if-Et3)#
vmtracer session
The vmtracer session command places the switch in the vmtracer mode for the specified session. The command creates a new session or loads an existing session for editing.
A VM Tracer session connects the switch to a vCenter server at a specified location, then downloads data about VMs and vSwitches managed by ESX hosts connected to switch ports. The switch supports a maximum of four VM Tracer sessions.
Configure VM Tracer session parameters in the vmtracer mode. Parameters configured in the vmtracer mode include the vCenter location and dynamic VLAN usage.
The no vmtracer session and default vmtracer session commands disable the session and remove the configuration from running-config.
Command Mode
Global Configuration
Command Syntax
vmtracer session name
no vmtracer session name
default vmtracer session name
Parameter
name The label assigned to the VM Tracer session.
- This command enters vmtracer mode for the system_1 session.
switch(config)# vmtracer session system_1 switch(vmtracer-system_1)# - This command disables the system_1 VM Tracer session. The system_1 session and removes all of the parameters from running-config
switch(config)#no vmtracer session system_1 switch(config)#
vrf
The vrf command allows the switch to communicate with a vCenter server by enabling VmTracer configuration mode. By default, VmTracer is enabled only in the default vrf command.
Command Mode
Vmtracer Configuration
Command Syntax
vrf vrf_name
Parameter
vrf_name specifies information of the corresponding VRF.
Example
switch(config)# vmtracer session system_1
switch(config-vmtracer-session-system_1)# vrf vrf1
switch(config-vmtracer-session-system_1)#vxlan
The vxlan command places the switch in the vmtracer-vxlan configuration mode. To monitor VXLAN based VMware configurations, the switch must communicate with a NSX for vSphere® (NSX-V). The vmtracer-vxlan configuration mode specifies the location and user account data that allows the switch to access a NSX-V within the configuration mode vmtracer session. Each VM Tracer session can be associated with one NSX-V instance.
The no vxlan and default interface vxlan commands delete the NSX-V instance from the configuration mode vmtracer session by removing all of the vmtracer-vxlan mode commands from running-config.
Command Mode
Vmtracer Configuration
Command Syntax
vxlan
no vxlan
default vxlan
Related Command
The vmtracer session command places the switch in the vmtracer configuration mode.
Example
switch(config)# vmtracer session vnet-1
switch(config-vmtracer-vnet-1)# vxlan
switch(config-vmtracer-vnet-1-vxlan)#